8 Home Remedies For Bug Bites, Signs, Symptoms, & Risk Factors
Those pesky bugs are everywhere! It will be helpful to keep these natural cures handy.

Image: Shutterstock
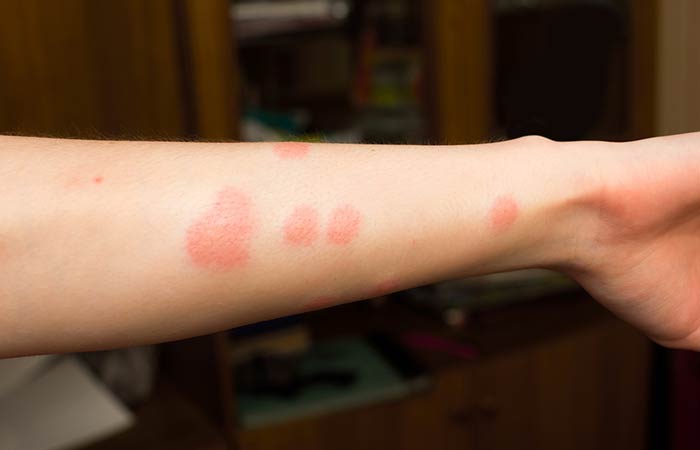
Be it spiders, bees, ticks, mosquitoes, or chiggers, insect bites are unpleasant. The bug bites not only hurt; they may even cause skin problems. And if they wind up activating the immune system, it might have profound implications. You can try simple home remedies for minor bug bites. However, if a bug bite appears to be serious or causes other medical symptoms, see a doctor right away. In this article, we will look at the signs, types, causes, and risk factors for bug bites. Additionally, we will also explore some of the different treatment options and tips to avoid bug bites in the long run. Scroll down to read further.
In This Article
Signs And Symptoms
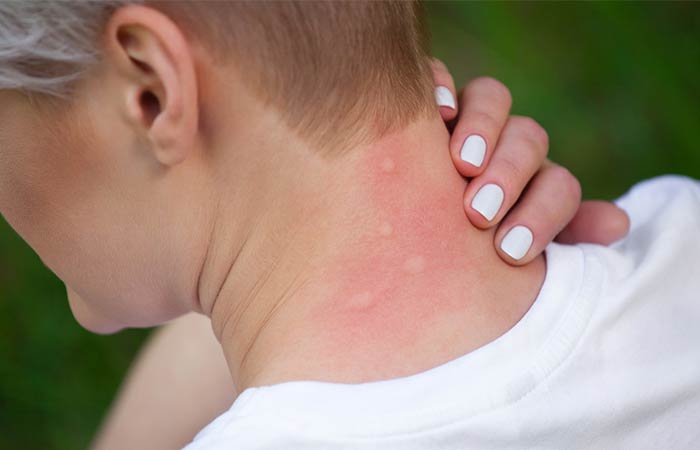
Bites from insects like mosquitoes and bees can trigger mild symptoms. The initial contact can be painful, and this is usually followed by an allergic reaction to the substance deposited by the insect on your skin.
While most of these encounters hardly cause anything more than minor discomfort, a few cases can be quite lethal if you are extremely allergic to the deposits of the insect on your skin.
The common symptoms of an insect bite include:
- Swelling
- A rash or redness
- Pain in the affected area
- Heat on and/or around the site of the bite or sting
- Itchiness
- Tingling sensation in the bitten area
- Numbness
Other symptoms that may call for a medical emergency are:
- Fever
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Unconsciousness
- Confusion
- Muscle spasms
- Rapidly beating heart
- Swollen lips and/or throat
If you end up developing flu-like symptoms in the days following an insect bite, see your doctor immediately to rule out the possibility of any infection that you may have contracted from the insect.
The following section will give you an idea of the different types of insect bites and their allergic reactions on the skin.
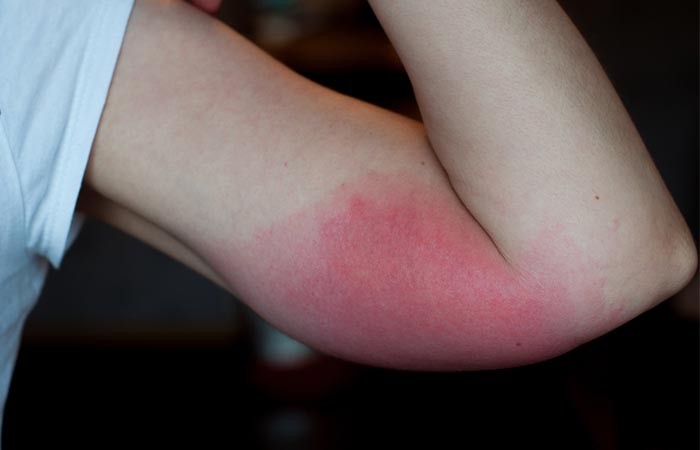
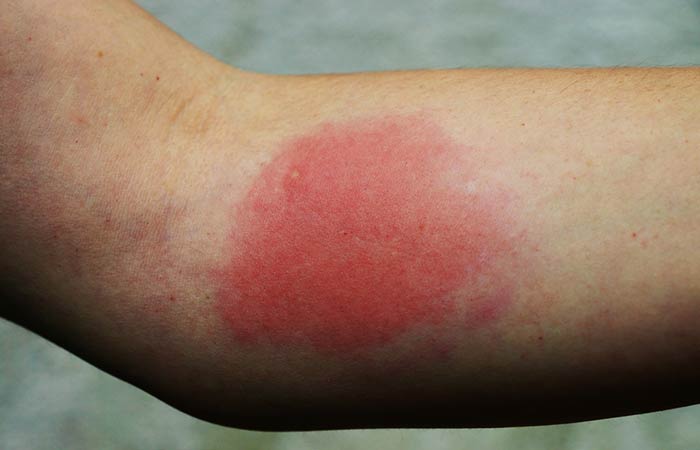
Pictures Of Different Types Of Insect Bites
1. Mosquito Bite
A mosquito bite has the following characteristics:
- The bite may be small, puffy, and round.
- The bump can look red, swollen, and itchy.
There could be multiple bites in the same area.
2. Fire Ant Bite
Fire ant bites may require immediate medical attention. They
- Are swollen and red
- May develop a blister
- Can sting, burn, itch, and may last up to a week
- Can cause an allergic reaction in some individuals, which may result in swelling, itching, and breathing difficulties
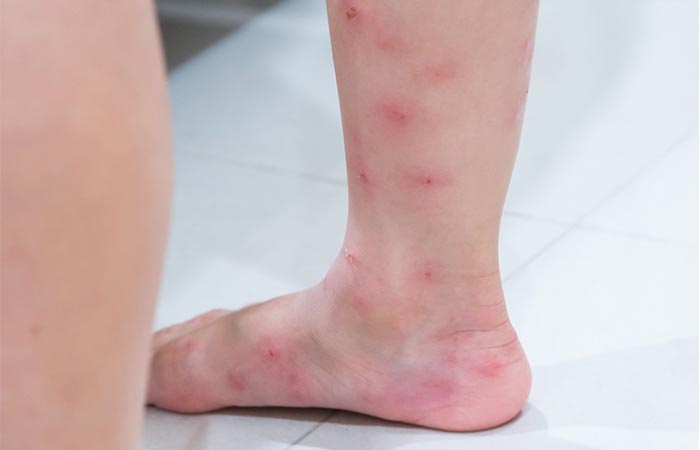
3. Flea Bite
Flea bites are:
- Found in clusters in the lower legs and feet
- Itchy and red, often surrounded by a red halo
The symptoms surface almost immediately post being bitten.
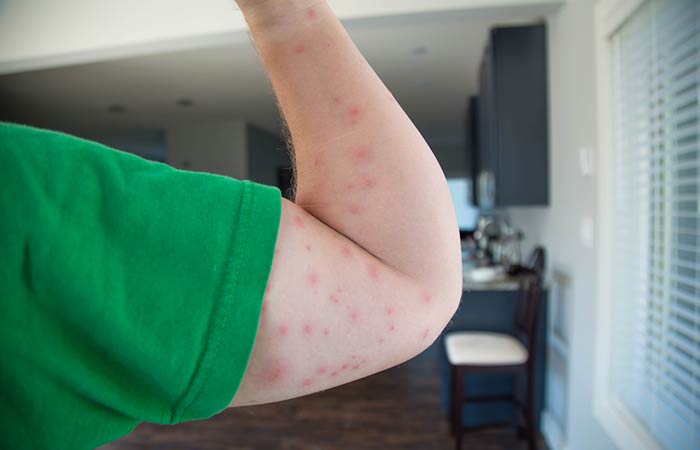
4. Bedbug Bite
Bedbug bites can cause an itchy rash that may:
- Be red and swollen with a dark-red center
- Appear in a line or in groups
- Result in itchy hives or blisters
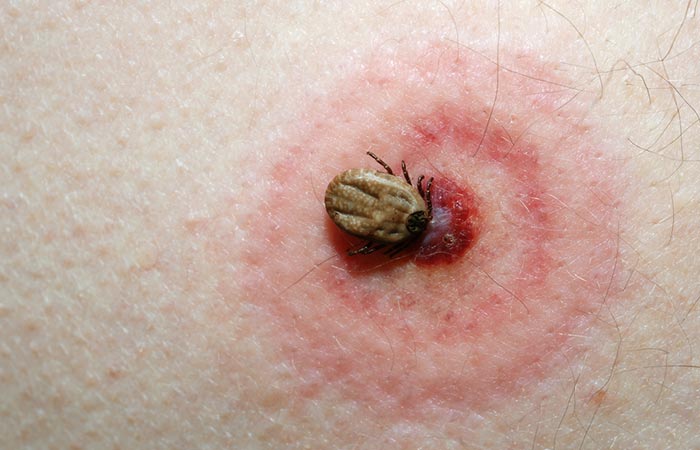
5. Tick Bite
The symptoms of a tick bite are as follows:
- It may cause swelling and pain.
- It can lead to the formation of a rash.
- Other reactions may include a burning sensation, formation of blisters, and/or difficulty in breathing.
- The tick often remains attached to the bite site for a long time.
- The bites rarely occur in groups..
6. Bee Sting
A bee sting can cause:
- Redness, swelling, and pain
- Itchiness
- A white spot at the site of the sting
Interestingly, a bee can only sting once.
7. Wasp Sting
The symptoms associated with a wasp bite are:
- Redness, swelling, burning, itching, and sharp pain at the affected site
- A raised welt around the affected site
Wasps can sting an individual multiple times.
What causes these allergic reactions from insect bites? Let’s find out.
What Causes Reactions To Bites And Stings?
When an insect bites or stings you, its venom gets injected into your body. This foreign substance causes your immune system to respond. The immediate reaction of your body to this invasion is mild redness and swelling at the affected site. It is also why bug bites itch as part of the same immune response.
In people who are extremely sensitive to an insect’s venom, the injected venom can also result in a potentially fatal condition called anaphylactic shock. This can cause your throat to tighten and may make it difficult for you to breathe.
If the venom happens to contain any infectious agents, it can also cause infections.
Let us now understand which people are at high risk of getting bug bites.
Risk Factors
Almost anybody can get an insect bite as such occurrences are very common.
Your risk may increase if you spend most of your time outdoors. Your risk also increases if you are visiting the woods or a rural village that has a lot of bugs and insects in the surroundings.
Your age is another risk factor for bug bites as older adults and children exhibit more severe reactions.
 Quick Tip
Quick TipIf you develop flu-like or allergic symptoms following an insect bite, it is best to see a doctor to get a medical diagnosis for your condition.
Diagnosis For Bites And Stings
It is recommended that you preserve the insect if it happens to die after biting or stinging you. However, do not provoke an insect if it is in the attacking mode – like in the case of honey bees.
Preserving the insect becomes important if it is poisonous, like some species of spiders. Some spider bites may release a dangerously potent venom that can cause severe symptoms. In such situations, preserving the bug can help your doctor diagnose your symptoms faster.
Once the cause of your symptoms is established, your doctor may then move on to prescribing suitable treatment options.
Treatment
Most bug or insect bites can be easily treated at home if the symptoms are mild and manageable. If a stinger is lodged in your skin, remove it and apply an ice pack to the stung area.
In some cases, your doctor may also prescribe a topical anti-itch cream, pain relievers, or antihistamine to manage the symptoms.
If the symptoms are severe, or if they are triggered by bites of poisonous insects like a scorpion or spiders like the black widow or brown recluse, contact emergency services immediately.
Bites or stings with milder symptoms can be treated right at home. The following are some home remedies that can help with the swelling, itching, and pain associated with most bug bites.
How To Get Rid Of Bug Bites Naturally
Home Remedies To Treat Bug Bites
1. Essential Oils
a. Tea Tree Oil
You Will Need
- 2 drops of tea tree oil
- 1 teaspoon of coconut oil or any other carrier oil
What You Have To Do
- Mix two drops of tea tree oil with a teaspoon of any carrier oil.
- Apply the mixture to the affected area and leave it on.
How Often You Should Do This
You can do this 1-2 times daily.
Why This Works
The anti-inflammatory nature of tea tree oil can help soothe the swelling and pain in the bug-bitten area (1). Its insect repellent properties can also prevent further bites or stings (2).
b. Neem Oil
You Will Need
- 1-2 drops of neem oil
- 1 teaspoon of coconut oil or any other carrier oil
What You Have To Do
- Add one to two drops of neem oil to a teaspoon of any carrier oil.
- Mix well and apply it to the affected area.
- Leave it on until it dries.
How Often You Should Do This
You may do this 1-2 times daily.
Why This Works
Neem oil and other neem formulations are quite popular insect repellents, especially in the case of mosquitoes (3). Its anti-inflammatory properties can also soothe the swelling and inflammation caused by insect bites (4).
In addition to these essential oils, you may also try lavender, chamomile, calendula, witch hazel, peppermint, and eucalyptus to help treat bug bites (5), (6), (7), (8), (9).
2. Baking Soda
You Will Need
- 1 teaspoon of baking soda
- 3 teaspoons of water
- Cotton balls
What You Have To Do
- Mix a teaspoon of baking soda with three teaspoons of water.
- Dip a cotton ball into this solution and apply it to the affected area.
- Leave it on until it dries completely.
How Often You Should Do This
You can do this 2-3 times daily.
Why This Works
Baking soda or sodium bicarbonate is an age-old home remedy to relieve insect bites (10). Its alkaline nature can help relieve the itchiness and inflammation in the affected area.
3. Apple Cider Vinegar
You Will Need
- 1 tablespoon of apple cider vinegar
- 1 tablespoon of water
- Cotton balls
What You Have To Do
- Mix a tablespoon of apple cider vinegar with a tablespoon of water.
- Dip a cotton ball into the mixture.
- Apply the mixture to the affected area.
- Leave it on for at least 20-30 minutes before rinsing it off with water.
How Often You Should Do This
You may do this 2-3 times daily.
Why This Works
The anti-inflammatory nature of apple cider vinegar can help reduce swelling in the affected area, and its antimicrobial activities can prevent further infection (11), (12).
4. Aloe Vera
You Will Need
- Freshly extracted aloe vera gel (as required)
- Cotton swabs
What You Have To Do
- Using a cotton swab, apply some aloe vera gel directly to the affected area.
- Leave it on for at least 30 minutes before rinsing it off.
How Often You Should Do This
You may do this 2-3 times daily.
Why This Works
The soothing and anti-inflammatory nature of aloe vera gel (herbal remedy) can help in alleviating inflammation, swelling, and pain associated with bug or insect bites (13).
5. Honey
You Will Need
- 1 teaspoon of organic honey
- Cotton swabs
What You Have To Do
- Dip a cotton swab into a teaspoon of organic honey.
- Apply it to the affected area. Leave it on for 30 minutes.
- Rinse it off with water.
How Often You Should Do This
You can do this multiple times daily.
Why This Works
Honey possesses significant anti-inflammatory properties and is a popular home remedy that can help in soothing insect bites (14), (10).
6. Rubbing Alcohol
You Will Need
- Rubbing alcohol (as required)
- Cotton balls
What You Have To Do
- Soak a cotton ball in rubbing alcohol.
- Apply it to the affected area.
- Leave it on.
How Often You Should Do This
You can do this 1-2 times daily.
Why This Works
Rubbing alcohol is used topically to relieve the itching caused by insect bites and prevent any further microbial infections at the affected site (10).
7. Turmeric
You Will Need
- 1 teaspoon of turmeric powder
- A little water
What You Have To Do
- Add a little water to a teaspoon of turmeric powder.
- Mix well to form a thick paste.
- Apply the paste to the affected area and leave it on for 20-30 minutes.
- Rinse it off.
How Often You Should Do This
You can do this 1 to 2 times daily.
Why This Works
The active component of turmeric is curcumin. Curcumin possesses anti-inflammatory and soothing properties that can relieve the symptoms of an insect bite (15). Additionally, it also has insect-repellent properties (16).
8. Oatmeal
You Will Need
- 1 tablespoon of powdered oatmeal
- 1 tablespoon of warm water
- A clean washcloth
What You Have To Do
- Make a paste by mixing the oatmeal and water in a bowl. If you need more paste, just ensure you add an equal ratio of oatmeal and water.
- Apply the paste on the affected areas and press down with the washcloth for 5-10 minutes.
- Wipe the area clean.
How Often You Should Do This
You can do this as many times as required.
Why This Works
Oatmeal contains phenolic compounds that have antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-itching properties (17). This makes oatmeal a popular soothing, anti-irritant ingredient for relieving the discomfort caused by bug bites.
These remedies can definitely help alleviate the symptoms of bug bites.
However, if you want to steer clear of bug bites altogether, listed below are some prevention tips that may help.
Tips To Avoid Bug Bites And Stings
When you are outdoors, consider the following:
- Be cautious when you are near nests or hives and hire professionals to get rid of them.
- Wear clothing that covers your body fully.
- Avoid floral patterns. Wear neutral colors.
- Avoid using perfumes and scented lotions.
- Keep all the eatables and drinks covered.
- Use an insect repellent.
 Quick Tip
Quick TipAs you can see, a little caution can go a long way when it comes to preventing insect bites, especially if your occupation requires you to be out in the open constantly.
Did this post address all your queries about insect bites? Share your thoughts and feedback with us in the comments section below.
Infographic: How To Prevent Bug Bites – A Few Tips
Bugs and insects carry all sorts of germs and diseases with them. Not to mention the constant itchiness you feel when bit.
Follow simple steps to avoid getting bug bites, like practicing good hygiene. Check out the infographic below to learn a few tips on preventing bug bites. Illustration: StyleCraze Design Team
Bug bites, though often mild and negligible, may cause moderate to severe allergic symptoms in some individuals. Depending on how your body reacts to the foreign deposits made by an insect on your skin, you may experience swelling, rashes, redness, itchiness, tingling, or numbness at the site of the bite. Not all bug bites look, feel or cause the same reaction, so it is important to identify the insect that has bit you. Home remedies for bug bites can effectively treat the pain, swelling, or itching associated with most insect bites that are mild. However, if you have been bitten by a poisonous insect or experience any of the serious symptoms such as muscle spasms, vomiting, fever, etc., following an insect bite, consult your healthcare provider immediately.
Frequently Asked Questions
How long does it take for bedbug bites to show?
While some people may develop a reaction within a few days of being bitten by bedbugs, for some, the symptoms may not develop for as long as 14 days.
What insect bites cause swelling?
The reaction of insect bites usually depends on the type of insects and an individual’s sensitivity to the bite. Bites from insects like mosquitoes, fire ants, bedbugs, ticks, horseflies, wasps, and bees are known to cause swelling.
What is the best ointment for insect bites?
Over-the-counter antihistamines like diphenhydramine (Benadryl) and the popular Calamine lotion are often used to soothe the reaction from an insect bite.
Does toothpaste help bug bites?
Anecdotal evidence suggests using toothpaste can help soothe bug bites. The antiseptic properties of toothpaste may provide quick relief from bug bites.
Does Listerine help bug bites?
No. Listerine does not help treat bug bites.
Does hydrogen peroxide help bug bites?
Hydrogen peroxide has antiseptic and disinfectant properties (18). Therefore, it may help treat bug bites and soothe itching.
Does deodorant help bug bites?
No, deodorants cannot help treat bug bites. However, applying them may repel some insects.
How long does an infected bug bite take to heal?
Usually, bug bites take only a few days to heal. But the infected ones may take around 1-2 weeks.
Key Takeaways
- Swelling, rashes, itching, and numbness can result from bug bites.
- In severe cases, bug bites can lead to nausea, fever, confusion, and swollen lips.
- Honey, turmeric, neem oil, and apple cider vinegar are some effective solutions that can calm the skin after bug bites.
- To prevent insect bites, try wearing clothes that cover your whole body. Also, using insect repellents is a must.

Image: Stable Diffusion/StyleCraze Design Team
Learn cool tips to deal with bug bite itch! Get relief from pesky bug bites with the easy and effective tips provided in the following video.
References
Articles on StyleCraze are backed by verified information from peer-reviewed and academic research papers, reputed organizations, research institutions, and medical associations to ensure accuracy and relevance. Read our editorial policy to learn more.
- “Melaleuca alternifolia (Tea Tree) Oil: a Review of Antimicrobial and Other Medicinal Properties” Clinical Microbiology Reviews, US National Library of Medicine
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1360273/ - “Insecticidal and repellent effects of tea tree and andiroba oils on flies associated with livestock.” Medical and Veterinary Entomology, US National Library of Medicine
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/m/pubmed/25171605/ - “Mosquito repellent action of neem (Azadirachta indica) oil.” Journal of the American Mosquito Control Association, US National Library of Medicine
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/m/pubmed/8245950 - “Therapeutics Role of Azadirachta indica (Neem) and Their Active Constituents in Diseases Prevention and Treatment” Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine, US National Library of Medicine
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4791507/ - “Lavender and the Nervous System” Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine, US National Library of Medicine
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3612440/ - “Comparative Analysis of Phenolic Composition of Six Commercially Available Chamomile (Matricaria chamomilla L.) Extracts: Potential Biological Implications” International Journal of Molecular Sciences, US National Library of Medicine
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8508714/ - “Antibacterial activity and medical properties of Witch Hazel Hamamelis virginiana” Annals of Tropical Medicine and Public Health, ResearchGate
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/343678379_Antibacterial_activity_and_medical_properties_of_Witch_Hazel_Hamamelis_virginiana - “Behavioral Responses of the Common Bed Bug to Essential Oil Constituents” MDPI, US National Library of Medicine
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7926421/ - “Repellent Efficacy of Eucalyptus globulus and Syzygium aromaticum Essential Oils against Malaria Vector, Anopheles stephensi (Diptera: Culicidae)” Iranian Journal of Public Health, US National Library of Medicine
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8643535/ - “Home Remedy Use Among African American and White Older Adults” Journal of the National Medical Association, US National Library of Medicine
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4631220/ - “Anti-obesity and anti-inflammatory effects of synthetic acetic acid vinegar and Nipa vinegar on high-fat-diet-induced obese mice” Scientific Reports, US National Library of Medicine
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5532206/ - “Antimicrobial activity of apple cider vinegar against Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus and Candida albicans; downregulating cytokine and microbial protein expression” Scientific Reports, US National Library of Medicine
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5788933/ - “Aloe vera: Nature’s soothing healer to periodontal disease“ Journal of Indian Society of Periodontology, US National Library of Medicine
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/m/pubmed/9121170/ - “Honey and Health: A Review of Recent Clinical Research” Pharmacognosy Research, US National Library of Medicine
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5424551/ - “Anti-inflammatory properties of curcumin a major constituent of Curcuma longa: a review of preclinical and clinical research” Alternative Medicine Review, US National Library of Medicine
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/m/pubmed/19594223 - “Turmeric powder and its derivatives from Curcuma longa rhizomes: Insecticidal effects on cabbage looper and the role of synergists” Scientific Reports, US National Library of Medicine
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5090202/ - “A Review of Health-Beneficial Properties of Oats” Foods US National Library of Medicine
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8625765/ - “Evaluation of hydrogen peroxide-based disinfectants in a new resazurin microplate method for rapid efficacy testing of biocides” Journal of Applied Microbiology, US National Library of Medicine
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19302294/