9 Benefits Of Peanut Oil, Types, And Side Effects
From improving cognitive health to delaying signs of aging – this oil does it all!

Image: Shutterstock
The many benefits of peanut oil stem from its rich nutritional profile. It happens to be among the healthier cooking oils. It is believed to be low in cholesterol and trans fats, though more research is warranted. Most anecdotal evidence suggests that the oil could be a healthier alternative.
However, the oil may also have possible side effects. In this post, we will discuss both sides of the oil. We will also understand if peanut oil is really fit for use in cooking.
 Know Your Ingredient: Peanut Oil
Know Your Ingredient: Peanut OilWhat Is It?
A type of seed oil extracted from peanuts.
What Are Its Benefits?
May help improve heart and joint health, cognitive performance, reduce inflammation, enhance insulin production and reduce cancer risks. Topical application can help fight skin aging, dermatitis and boost hair growth.
Who Can Use It?
Suitable for use on all skin and hair types, except for people with a peanut allergy.
How Often?
Can be consumed daily in moderation.
Caution
May increase risk of heart disease and result in non-alcoholic fatty liver condition, unwanted weight gain, allergies, and inflammatory bowel disease.
In This Article
What Is Peanut Oil?
Peanut oil is often referred to as groundnut oil. It is a vegetable oil extracted from the seeds of the peanut plant.
Some believe that the goodness of peanut oil primarily boils down to its vitamin E content. Vitamin E is an antioxidant known to reduce free radical damage and cut heart disease risk (1).
What Are The Different Types Of Peanut Oil?
Peanut oil is available in different types:
- Refined peanut oil, which is refined, bleached, and deodorized. The process removes allergens in the oil, and this makes it safe for people with peanut allergies.
- Cold-pressed peanut oil, where the peanuts are crushed, and the oil is forced out. This one retains more flavor and nutrients.
- Gourmet peanut oil that is usually roasted and has an intense flavor.
- Peanut oil blend, where the oil is blended with another oil with a similar taste.
 Trivia
TriviaWhat Are The Benefits Of Peanut Oil?
1. May Promote Heart Health

Peanut oil contains vitamin E (2). Studies show that this vitamin can fight free radicals, which may cause heart disease (3).
The oil is also rich in monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats (2). These are linked to a lowered cardiovascular disease risk. As per the American Heart Association, these types of fats can reduce heart disease risk by as much as 30% (4).
Some anecdotal evidence suggests that the oil may also lower bad cholesterol levels. However, more research is needed to support this statement.
2. May Enhance Cognitive Health
There is no direct research stating that peanut oil may promote cognitive health. However, the vitamin E it contains may play a role.
Studies show that vitamin E may promote healthy brain aging in the elderly. The nutrient may also reduce the risk of Alzheimer’s diseasei XA progressive disease that occurs due to the degeneration of neurons in the brain, which causes dementia and impaired cognitive functions. (5).
Vitamin E supplementation was also found to boost motor activities in individuals (5).
3. May Improve Insulin Sensitivity
Peanut oil contains oleic acid, which was found to improve insulin production in type 2 diabetes. A diet high in peanut oil can also reverse the negative effects of inflammation on type 2 diabetes (6).
Peanut oil also contains polyunsaturated fatty acids. These are healthy fats. Studies show that PUFAsi XPolyunsaturated fatty acids are fats that are important for nerve function and are commonly found in vegetable oils and seeds. may improve blood glucose levels, treat insulin resistance, and enhance insulin secretion capacity. Replacing dietary saturated fat with polyunsaturated fat improved insulin secretion in those with diabetes (7).
A combination of monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats (as present in peanut oil) may also enhance insulin sensitivity in individuals with diabetes.
4. May Help Reduce Cancer Risk
Peanut oil contains phytosterolsi XNatural compounds found in plants that help lower blood cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseases. , compounds recognized for their potential anticancer properties. These compounds might reduce the risk of the cancers of the prostate and colon. Some research states that they may reduce the risk of breast cancer (8).
Phytosterols, in general, have also been studied for their anticancer effects. Emerging evidence states that these compounds may inhibit the cancers of the lung, stomach, and ovaries (9).
Some believe that the polyphenol antioxidants in peanut oil fight free radicals, which may contribute to cancer prevention. Peanut oil may act as a natural tonic that may boost immune levels.
5. May Help Relieve Joint Pains
Peanut oil contains polyunsaturated fatty acids (2). Studies state their therapeutic potential in treating joint pains in the case of rheumatoid arthritisi XA chronic autoimmune disease that causes inflammation of the joints in the hands and legs, which can gradually lead to bone erosion. (10).
The oil could be used to relieve debilitating joint pains. Peanut oil is applied to the skin directly and massaged well, and this may offer some relief. However, there is insufficient information on the topical application of peanut oil. Please consult your doctor before you use the oil for this purpose.
Insufficient Evidence For The Following
6. May Delay Signs Of Aging
There is no direct research stating that peanut oil may delay the signs of aging. However, some research states that the vitamin E in the oil could help in this regard (11).
Vitamin E is an important ingredient in most over-the-counter anti-aging products (11).
Vitamin E also fights the adverse effects of oxidative stress. Some of these effects include photoaging (which is the accelerated aging of the skin with the influence of UV radiation) (12).
Applying peanut oil topically may offer anti-aging benefits, though there is no research to prove this. The vitamin E it contains may fight free radicals, which may otherwise accelerate aging signs like wrinkles and fine lines.
7. May Treat Dry Skin
Topical vitamin E may improve the symptoms of atopic dermatitis. The condition is characterized by red and itchy skin, sometimes accompanied by dry skin (13).
A study conducted on 2.1 million patients found that the lifetime prevalence of atopic dermatitis in the Australian general practice population was 16.4%. Its prevalence was higher in females (17.3%) than in males (15.3%). Furthermore, the study found that 1 in 5 patients who suffered from the condition had moderate‐to‐severe symptoms of the disease.
The topical application of peanut oil could help treat dry skin, but research is limited. Some believe the oil also has moisturizing properties that could help. You can apply the oil to your face and other affected areas and leave it on for about 20 minutes. Take a bath as usual.
8. May Boost Hair Growth
Some research suggests that the ingestion of vitamin E supplements may boost hair growth (14). But there is limited information if the same effect could be achieved with topical application.
Some believe that the topical application of vitamin E may reduce protein loss from hair and make it thicker. The oil is also thought to moisturize split ends and regenerate damaged hair.
9. May Help Treat Scalp Psoriasis
Some studies state that vitamin E may aid the treatment of psoriasis, including that of the skin and scalp (15).
Anecdotal evidence suggests that the antioxidants in peanut oil may treat dandruff, and in some cases, can aid the treatment of scalp psoriasis. This could be attributed to the moisturizing properties of peanut oil.
How Else Can Peanut Oil Be Used?
There are different ways peanut oil can be used:
- Cooking
Peanut oil is low in saturated fats and rich in monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats. This is why it is ideal for cooking. It works particularly well with Asian foods that are predominantly prepared in the wok.
- Making Soap
You can also use the oil to make soap. Thanks to its conditioning properties, the soap can boost skin health. One downside is that the oil may not last long in your soap as it can turn rancid quite fast.
- Making Biodiesel
Peanuts are more than 50% oil, which is why one acre of them produces about 123 gallons of oil. Though this alternative fuel is slightly expensive, it might be where the future lies.
- Vaccines
In fact, this has been happening since the 1960s. The oil was used in influenza shots to lengthen immunity in patients.
 Trivia
TriviaThese are certain other ways peanut oil is used. Do you want to know what else the oil contains? Scroll down to the next section.
What Is The Nutritional Profile Of Peanut Oil?
One cup of peanut oil offers you 169% of the daily value of vitamin E. The following table shows the nutritional value of peanut oil in detail.
| Nutrition Facts Serving Size 216g | ||
|---|---|---|
| Amount Per Serving | ||
| Calories 1910 | Calories from Fat 1910 | |
| % Daily Value* | ||
| Total Fat 216g | 332% | |
| Saturated Fat 36g | 182% | |
| Trans Fat | ||
| Cholesterol 0mg | 0% | |
| Sodium 0mg | 0% | |
| Total Carbohydrate 0g | 0% | |
| Dietary Fiber 0g | 0% | |
| Sugars 0g | ||
| Protien 0g | ||
| Vitamin A | 0% | |
| Vitamin C | 0% | |
| Calcium | 0% | |
| Iron | 0% | |
| Calorie Information | ||
| Amounts Per Selected Serving | %DV | |
| Calories | 1910(7997 kJ) | 95% |
| From Carbohydrate | 0.0(0.0 kJ) | |
| From Fat | 1910(7997 kJ) | |
| From Protein | 0.0(0.0 kJ) | |
| From Alcohol | 0.0(0.0 kJ) | |
| Fats & Fatty Acids | ||
| Amounts Per Selected Serving | %DV | |
| Total Fat | 216 g | 332% |
| Saturated Fat | 36.5 g | 182% |
| Monounsaturated Fat | 99.8 g | |
| Polyunsaturated Fat | 69.1 g | |
| Total trans fatty acids | ~ | |
| Total trans-monoenoic fatty acids | ~ | |
| Total trans-polyenoic fatty acids | ~ | |
| Total Omega-3 fatty acids | ~ | |
| Total Omega-6 fatty acids | 69131 mg | |
| Vitamins | ||
| Amounts Per Selected Serving | %DV | |
| Vitamin A | 0.0 IU | 0% |
| Vitamin C | 0.0 mg | 0% |
| Vitamin D | ~ | ~ |
| Vitamin E (Alpha Tocopherol) | 33.9 mg | 169% |
| Vitamin K | 1.5 mcg | 2% |
| Thiamin | 0.0 mg | 0% |
| Riboflavin | 0.0 mg | 0% |
| Niacin | 0.0 mg | 0% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.0 mg | 0% |
| Folate | 0.0 mcg | 0% |
| Vitamin B12 | 0.0 mcg | 0% |
| Pantothenic Acid | 0.0 mg | 0% |
| Choline | 0.2 mg | |
| Betaine | 0.0 mg | |
Values sourced from U.S. Department of Agriculture, oil, peanut
Excess intake of peanut oil may cause certain side effects. We have discussed them in the next section.
Side Effects And Allergies Of Peanut Oil
- High Amount Of Omega-6 Fatty Acids
Peanut oil is high in omega-6 fatty acids. Though these fatty acids are important, their excess intake may cause issues. Omega-6 fatty acids tend to be pro-inflammatory in nature (16).
The typical Western diet consists of higher amounts of omega-6 fatty acids than omega-3 fatty acids. When this is the case, adding excess of peanut oil may further increase the levels of omega-6 fatty acids. This can increase the risk of cardiovascular disease, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, obesity, and inflammatory bowel disease (16).
- Allergies
Those having a peanut allergy may also develop an allergic response to the oil. Signs of these allergies include urticaria (a type of round skin rash), gastrointestinal and upper respiratory tract reactions, and anaphylaxisi XA severe, life-threatening response to an allergic reaction that occurs within seconds or minutes of exposure to an allergen. (17).
- The Oil Could Be Prone To Oxidation
The polyunsaturated fatty acids in the oil may be easily prone to oxidation. Merely heating the oil can result in this phenomenon. This oxidation can create free radicals that can cause harm to the body (also called oxidative damage). This may cause inflammation and damage the immune system (18).
Hence, using peanut oil regularly for cooking may not be a good idea especially if you are on a weight loss diet. You may want to go for a healthier option, like olive oil (extra virgin olive oil could be a better idea).
In case you are pregnant or breastfeeding, stick to normal amounts of peanut oil (after consulting your doctor). Don’t consume excess of it. Also, avoid the oil if you are allergic to peanuts, soybeans, and other related plants (members from the Fabaceae plant family).
Those allergic to peanut oil often consider going for canola oil. But how do the two compare? Learn more in the next section.
Peanut Oil Vs. Canola Oil
Canola oil, like peanut oil, is neutral with a mild flavor. It is ideal for those occasions when you do not want to add any extra flavor to your dish. Canola oil has a higher smoke point of 425-450°F (220–230°C), while peanut oil’s smoke point sits at 400°F (205°C). This makes both of them suitable for frying. Both oils also have similar calorific values. While 100 grams of peanut oil have 900 calories, 100 grams of canola oil have 884 calories (19), (20). You can use either of them as per your dietary preferences.
Learn the basics of healthy cooking oils with this informative video! Discover which oils are best for different cooking methods and how to use them for delicious meals.
Infographic: Top 7 Health Benefits Of Peanut Oil
Peanut oil has been used for centuries for its versatility and nutritious composition. This culinary plant oil can improve your general well-being, promote heart health, and give you healthy skin. Check out the infographic below to learn more about the top benefits of incorporating peanut oil into your daily routine.
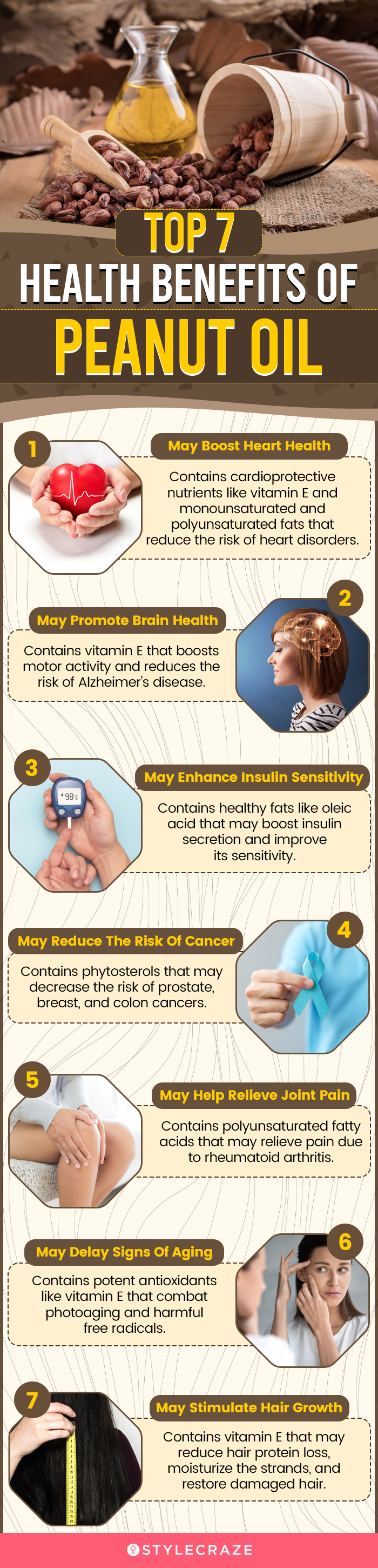
Illustration: StyleCraze Design Team
Peanut oil or groundnut oil is widely used as cooking oil. This high in energy oil is packed with vitamin E, essential minerals, and other nutrients that make it nutritious. Groundnut oil benefits the heart and brain. It also may reduce the risk of cancer and improve insulin sensitivity. Anecdotal evidence indicates that it can improve gut health and digestion and is effective topically as well. It may help moisturize skin and boost hair growth. Peanut oil can also be used to make soaps and biodiesel. However, excessive consumption may lead to a few side effects, including allergic reactions. Seek medical advice in such cases.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a good substitute for peanut oil?
Almond oil can be a good substitute, given it has a similarly high smoke point.
How long does peanut oil last?
Unopened peanut oil can last for about a year. But once opened, it lasts only for four to six months. It can get rancid after that.
Is peanut oil better than olive oil?
Though both are rich in polyunsaturated fatty acids, peanut oil has higher levels of omega-6 fatty acids. Hence, it may not be as healthy as olive oil in cooking. In terms of regular use, olive oil could be better than peanut oil.
How long does it take to heat peanut oil?
Peanut oil takes about 10 minutes to get heated.
What temperature does peanut oil boil at?
Peanut oil boils at about 450o F (also called smoke point).
Is frying in peanut oil healthier?
Peanut oil is unsuitable for high-heat cooking (like deep frying). The fats in the oil degrade when exposed to high heat and may adversely affect health.
Which is healthier, peanut oil or avocado oil?
Both are nutritious. However, polyunsaturated fatty acids in peanut oil make it less healthy than avocado oil, which has an excellent nutritional value at low and high temperatures (17).
Can you cook vegetables in peanut oil?
Yes, you can cook or saute vegetables in peanut oil at medium flame.
Is it OK to fry chicken in peanut oil?
Yes, you can fry chicken in peanut oil. However, do not use it for deep frying as the polyunsaturated fatty acids degrade and may affect your health.
Can you mix olive oil and peanut oil?
Yes, you can mix olive and peanut oil. However, the resultant oil will have the lower smoking point of the two.
Key Takeaways
- Peanut oil may benefit the heart and also lessen the risk of prostate and colon cancers.
- It has vitamin E which fights the harmful effects of oxidative stress and may also aid in anti-aging.
- The oil promotes hair growth and is believed to moisturize split ends and repair damaged hair.
- Do not consume it in excess as it may result in several side effects, such as allergies.

Image: Stable Diffusion/StyleCraze Design Team
References
Articles on StyleCraze are backed by verified information from peer-reviewed and academic research papers, reputed organizations, research institutions, and medical associations to ensure accuracy and relevance. Read our editorial policy to learn more.
- The Role of Vitamin E in Human Health and Some Diseases, Sultan Qaboos University Medical Journal, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3997530/?report=classic - Oil, peanut, salad or cooking, U.S. Department of Agriculture.
https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/171410/nutrients - Dietary Fats and Cardiovascular Disease: A Presidential Advisory From the American Heart Association, Circulation, American Heart Association.
https://ahajournals.org/doi/full/10.1161/cir.0000000000000510 - Effects of Vitamin E on Cognitive Performance during Ageing and in Alzheimer’s Disease, Nutrients, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4276978/?report=classic - Oleic acid and peanut oil high in oleic acid reverse the inhibitory effect of insulin production of the inflammatory cytokine TNF-alpha both in vitro and in vivo systems, Lipids in Health and Disease, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19558671 - Effects of Saturated Fat, Polyunsaturated Fat, Monounsaturated Fat, and Carbohydrate on Glucose-Insulin Homeostasis: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Randomised Controlled Feeding Trials, PlOS One.
https://journals.plos.org/plosmedicine/article?id=10.1371/journal.pmed.1002087 - Peanuts as a source of beta-sitosterol, a sterol with anticancer properties, Nutrition and Cancer, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10890036 - Anticancer effects of phytosterols, European Journal of Clinical Nutrition, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19491917 - Polyunsaturated fatty acids: any role in rheumatoid arthritis?, Lipids in Health and Disease, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5634864/ - Vitamin E in dermatology, Indian Dermatology Online Journal, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4976416/?report=classic - The role of vitamin E in normal and damaged skin, Journal of Molecular Medicine, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/7633944 - Effects of oral vitamin E on treatment of atopic dermatitis: A randomized controlled trial, Journal of Research in Medical Sciences, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4755091/?report=classic - Effects of Tocotrienol Supplementation on Hair Growth in Human Volunteers, Tropical Life Sciences Research, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3819075/?report=classic - Efficacy of nutritional treatment in patients with psoriasis: A case report, Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4533159/?report=classic - Health Implications of High Dietary Omega-6 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids, Journal of Nutrition and Metabolism, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3335257/?report=classic - Allergy to peanut oil–clinically relevant?, Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17373969 - Oxidative stress, inflammation, and cancer: How are they linked?, Free Radical Biology & Medicine, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2990475/ - Avocado Oil: Characteristics, Properties, and Applications, Molecules, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6600360/ - Peanut oil, US Department of Agriculture.
https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/2345744/nutrients - Oil, canola, US Department of Agriculture.
https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/172336/nutrients































