6 Benefits Of Linden Tea, How To Prepare It, & Side Effects
Relax with a cup of nourishing herbal tea that will help improve your gut health.

Image: iStock
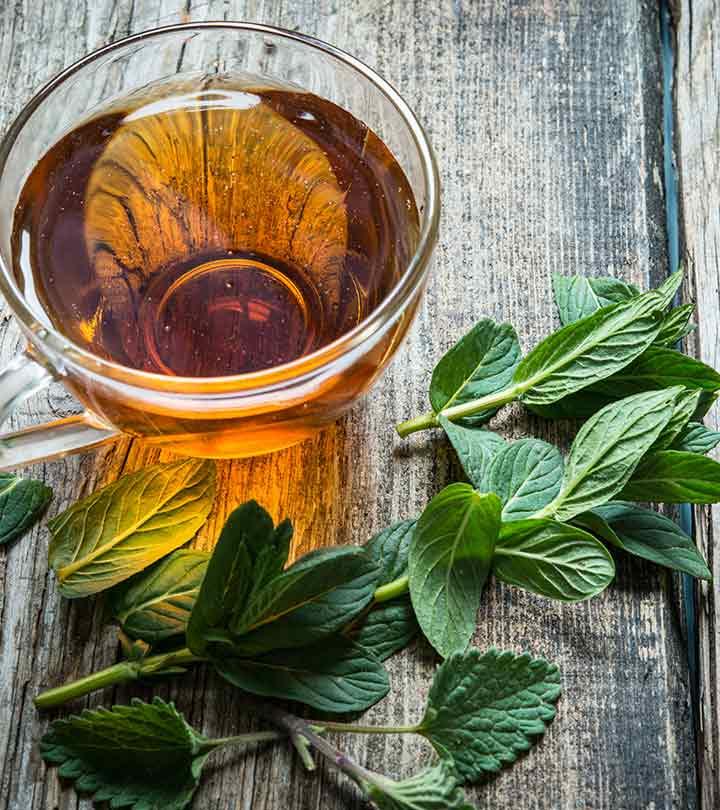
Doesn’t it feel nice and warm to curl up with a steaming cup of freshly brewed tea? If you are looking for a non-caffeinated herbal tea to help you relax, you can add linden tea to your list. Linden tea benefits you in multiple ways. It is an herbal tea made by brewing the dried flowers, leaves, and bark of the linden tree (a variety of lime trees). Apart from its great taste and wonderful aroma, linden tea also has been used for medicinal purposes for hundreds of years. Want to learn more about its benefits? Read on to explore more.
In This Article
What Is Linden Tea?
Linden is an herb that comes from various species of Tilia, or lime tree, widely found in the temperate regions of Europe, North America, and northern parts of Asia. It has been used in folk medicine for centuries to treat a wide range of health problems. Flowers from two specific linden species (Tilia cordata and Tilia platyphyllos) are used to soothe the nerves, help ease anxiety, irregular heartbeats, and stomach disorders. Today, linden is commonly used in many cough and cold remedies as well (1).
 Trivia
TriviaActive ingredients found in the flowers, bark, and leaves of the linden tree provide you with many key health benefits. Let us now understand these health benefits in detail.
Benefits Of Linden Tea
- May Promote Sleep And Relaxation
Linden tea extracts might help calm your nerves, relax and unwind. Research suggests active linden components mimic GABA, a chemical found in the brain that helps you calm down and feel relaxed (2).
Animal studies also suggest the sedative properties of linden extracts making it a good addition to your bedtime routine (3), (4).
- May Help Fight Inflammation
Inflammation may lead to many long-term health issues including cancer and diabetes (5). Quercetin, kaempferol, and tiliroside are powerful antioxidants found in the flowers and buds of linden trees that act on the toxic free radicals in your body and help reduce inflammation (6), (7).
 Pro Tip
Pro TipWhile these studies are promising, the amount of antioxidants in different blends of the tea may vary as per the time infused and the use of loose tea vs tea bags (9). So, further research is warranted to prove its efficacy.
- May Reduce Mild Pain
Quercetin and tiliroside may also help reduce mild pain and swelling (7), (10). In one study, mice with swollen paws were given a particular measure of tiliroside as per their body weight. This resulted in a 27% and 31% reduction in the swelling and pain respectively (6).
In another study, women suffering from the pain and discomfort of rheumatoid arthritis were asked to supplement their diet with quercetin. They reported a significant improvement in their symptoms, pain, and inflammation (11). However, the amount of these antioxidants found in linden tea varies as per the brand and blend, requiring further research to determine the same.
- May Have Diuretic Effects
Linden tea components might have diaphoretic and diuretic effects which means they help flush out excess fluids from the body and promote sweating. Linden tea infusions are commonly used in places like Germany to treat cold and cough in adults and children above 4 years of age (1). This could be because of the combined effects of kaempferol, quercetin, and p-coumaric acid. However, scientific evidence to establish this diuretic effect of linden is limited.
- May Help Lower Blood Pressure
Linden tea contains a few important bioactive plant compounds that might help lower blood pressure (1), (6). Animal studies have shown that the antioxidant tiliroside found in linden tea might help regulate your heart’s muscular contractions and reduce systolic blood pressure (6), (12). However, the mechanism behind this is still unknown and more research is warranted to establish this connection. Also, you should not use linden tea as a replacement for any heart medications.
- Soothes Your Digestive Tract
The comforting warm hydration from this herbal, caffeine-free tea may help aid the passage of food through your intestines, relieving you of any stomach discomfort. However, more research is needed to establish a direct link.
Now that you are aware of the many benefits of linden tea, you must be tempted to brew yourself a cup of this warm comforting tea.
How To Prepare Linden Tea?
Linden tea with its relaxing effect might be a good addition to your unwinding routine at the end of the day. Let’s see how you can prepare a cup for yourself.
- Put about 1g of loose linden tea into an infuser.
- Boil 150 ml water in the kettle.
- Put the infuser with tea leaves in a cup.
- Add freshly boiled water to the cup.
- Allow the leaves to steep in the water for 5-10 minutes. You can let it brew longer for a stronger taste.
- You may add in some lemon or honey as per your preference.
During the hot summers, you can also steep a few linden tea bags in warm water, cool and leave them in the fridge overnight to relish some refreshing ice tea in the hot afternoons.
Anca, a blogger, uncovers the delightful secret of linden tea and its nostalgic connection to her childhood in Romania. She mentions, “Linden tea is probably the closest thing to the British idea of tea. Not for the taste, far from it, but for fulfilling that need of comfort and refreshment, in sickness and in health (i).”
While having a cup of linden tea might seem soothing and harmless, it can easily be overdone. You should thus be aware of its possible risks as well.
Precautions And Side Effects
The FDA and European Medicines Agency consider linden flowers as GRAS (generally recognized as safe) for moderate consumption (13), (14). Still, there are a few things you need to keep in mind before adding linden to your daily diet.
- Might Interact With Certain Medications
Since linden tea might act as a diuretic in flushing out excess salt and fluids from your body, you should avoid taking it along with any other diuretic medicine or food sources to prevent dehydration (1).
- May Cause Botulism
Linden might carry some amount of Clostridium botulinum spores, which can cause botulism (a rare but paralyzing and even life-threatening illness). While it doesn’t contain a significant amount, you should avoid giving it to babies and infants as it increases the risks of infant botulism (15).
- Might Not Be Safe For Pregnant Women Or Children
The safety of linden tea for breastfeeding and pregnant women is still unknown nor has it been tested or deemed safe for children yet. So, children should not be given linden tea and lactating and pregnant women should also avoid it (1).
- Might Cause Drowsiness
While the sedative properties of linden can help you relax, the resulting drowsiness might not be suitable while driving, operating any heavy machinery, or working in general (1). You should avoid linden tea in situations where you need to be alert and attentive.
- Might Aggravate Allergy
If you have a pollen allergy, you should be careful of allergic symptoms while having linden tea (1). The pollen in linden flowers might cause your allergy to flare up.
Linden tea benefits your body in a number of ways. It is loaded with many beneficial nutrients, vitamins, and minerals. Linden tea is good for your immunity as it may relieve cough and cold. It has anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties that may provide relief from pain and reduce swelling. Linden tea may help you relax and aid in sleep. Nevertheless, excessive consumption may have side effects. It may cause drowsiness, botulism, or interfere with diuretic medications. If you experience any side effects, limit your consumption and seek medical advice.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is linden tea acidic?
No, linden herbal tea is alkaline.
Can I mix linden and chamomile teas?
Yes, you can combine linden tea and chamomile tea to enjoy a relaxing tea infusion.
Does linden tea have caffeine?
Linden tea is naturally caffeine-free. Unlike teas derived from the Camellia sinensis plant (such as black, green, or white tea), which naturally contain caffeine, linden tea originates from the flowers of the linden tree (Tilia genus) and doesn’t naturally contain caffeine. It is an herbal infusion appreciated for its soothing properties and is often preferred as a caffeine-free alternative, suitable for those seeking a calming beverage without the stimulating effects of caffeine.
Key Takeaways
- Found in the temperate regions of Europe, North America, and northern parts of Asia, linden is an herb that belongs to species of Tilia, or lime tree.
- It may promote sleep and relaxation, fight inflammation, and reduce mild pain.
- However, it may cause botulism, drowsiness, and aggravate allergy.
Experience the magic of Linden tea in this informative video! Find out how it reduces anxiety, pairs deliciously with honey, and the unexpected side effects you need to keep in mind while including this in your diet. Click play now!
Personal Experience: Source
StyleCraze's articles are interwoven with authentic personal narratives that provide depth and resonance to our content. Below are the sources of the personal accounts referenced in this article.
(i) One of nature’s best kept secrets: linden teahttps://whitenosugarblog.wordpress.com/2018/06/26/one-of-natures-best-kept-secrets-linden-tea/
References
Articles on StyleCraze are backed by verified information from peer-reviewed and academic research papers, reputed organizations, research institutions, and medical associations to ensure accuracy and relevance. Read our editorial policy to learn more.
- Assessment report on Tilia cordata Miller Tilia platyphyllos Scop Tilia x vulgaris Heyne or their mixtures flos
https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/herbal-report/final-assessment-report-tilia-cordata-miller-tilia-platyphyllos-scop-tilia-x-vulgaris-heyne-their_en.pdf - Bud extracts from Tilia tomentosa Moench inhibit hippocampal neuronal firing through GABAA and benzodiazepine receptors activation
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26144285 - Flavonoids from Tilia americana with anxiolytic activity in plus-maze test
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18539420 - Pharmacological evaluation of the anxiolytic and sedative effects of Tilia americana L. var. mexicana in mice
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16930893 - The inflammation theory of disease
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3492709 - A Review on the Dietary Flavonoid Tiliroside – Grochowski – 2018 – Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1111/1541-4337.12389 - Flavonoids with antinociceptive and anti-inflammatory activities from the leaves of Tilia argentea (silver linden)
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15507365/ - Hepatoprotective and antioxidant activity of linden (Tilia platyphyllos L.) infusion against ethanol-induced oxidative stress in rats
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24337514/ - Effect of different brewing times on antioxidant activity and polyphenol content of loosely packed and bagged black teas (Camellia sinensis L.)
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC4930538/ - Quercetin and derivatives: useful tools in inflammation and pain management
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27995808 - The Effect of Quercetin on Inflammatory Factors and Clinical Symptoms in Women with Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Double-Blind Randomized Controlled Trial
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27710596 - Mechanism of the antihypertensive and vasorelaxant effects of the flavonoid tiliroside in resistance arteries
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23877918 - CFR – Code of Federal Regulations Title 21
https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cdrh/cfdocs/cfcfr/cfrsearch.cfm?fr=182.10 - Assessment report on Tilia cordata Miller Tilia platyphyllos Scop Tilia x vulgaris Heyne or their mixtures flos
https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/herbal-report/final-assessment-report-tilia-cordata-miller-tilia-platyphyllos-scop-tilia-x-vulgaris-heyne-their_en.pdf - Linden flower (Tilia spp.) as potential vehicle of Clostridium botulinum spores in the transmission of infant botulism
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20085187/