Galveston Diet – Benefits, Food List, & How Does It Work
The dynamic duo of intermittent fasting and an anti-inflammatory diet save the day.

Menopause can cause a significant shift in hormones, weight, and body composition. The Galveston diet seeks to restore this disrupted hormonal balance while helping you maintain a stable weight. The emphasis on anti-inflammatory meals, nutrient-rich antioxidant-loaded foods, and portion control makes this diet stand out from other approaches. It focuses on developing healthy eating habits that are easy to sustain. This eating plan, developed by a renowned Houston-based board-certified OBGYN and nutrition expert, Dr. Mary Claire Haver, could just be the ticket for the smooth fitness journey you were waiting for. Take advantage of her expertise and uncover the most uncommon secrets to weight loss in this article. Keep reading!
 At A Glance: Galveston Diet
At A Glance: Galveston Diet- Principle: A balanced diet rich in healthy fats, lean proteins, anti-inflammatory and antioxidant foods, and low in carbs that helps reduce inflammation in the body
- Purpose: To reduce inflammation, body weight, and control blood sugar levels
- Who It Is For: People in perimenopause and menopause stages
- Duration: Short-term
- Who Should Avoid: People with high cholesterol levels and underweight individuals
- Cons: May cause fatigue, weakness, constipation, and nutritional deficiencies
In This Article
What Is The Galveston Diet?

The Galveston diet is a science-backed lifestyle plan proven to be effective in maintaining a healthy weight and general well-being.
The program’s creator, Dr. Mary Haver, is an experienced obstetrician-gynecologist. She developed this dietary regimen in response to her patients’ many queries concerning weight gain during menopause. While she always counseled her patients to eat less and exercise more, she didn’t realize such advice didn’t work until she herself experienced the changes associated with menopause. This epiphany ultimately motivated her to develop a new strategy.
Dr. Haver strongly endorses the countless advantages of intermittent fasting and feels that nutrition in the right proportions can reduce inflammation. In addition to increasing muscle mass and decreasing body fat, the program claims to steadily improve sleep patterns, reduce the frequency of hot flashes, and clear brain fogi XA group of symptoms that may impair your cognition and result in uncertainty, forgetfulness, and loss of focus. .
The Galveston diet’s anti-inflammatory concept helps specifically women achieve their health goals. Its focus on nutrition, exercise, and mindfulness has helped users take charge of their health by developing personal accountability.
This self-paced diet regimen is available at a one-time purchase ranging from $59 to $99 or a premium package that costs $49 per month. It also provides a variety of educational videos, reference materials, meal plans, progress-tracking tools, and individual sessions to help one stay motivated.
 Quick Tip
Quick TipTatiana Schloessman, a blogger, wrote about her experience of doing the Galveston diet to address her menopausal weight gain in her blog. She said, “When we finally get our eating and exercise habits onto the right path, our bodies immediately respond to the changes and hard work. The excitement is the “magic energy” that our bodies use to tone our muscles and burn extra calories (i)”.
The Galveston diet offers holistic and practical solutions that are easy to follow and capable of producing sustainable, long-term results. Read on to find out this diet’s underlying science and how it works.
Major Principles Of The Galveston Diet
The three major principles behind the Galveston diet are:
1. 16/8 Intermittent Fasting
It is a type of time-restricted fasting where individuals eat during an 8-hour window and fast for the remaining 16 hours. This is often done daily to achieve weight loss, improve health markers, and increase longevity. The most common approach is to eat during the day and fast overnight, although some people may choose to practice it otherwise. An online study conducted on 1241 Americans in 2020 found that 24% of the respondents had practiced or tried intermittent fasting. It was further noted that 50% found this diet to be very effective for weight loss while 37% found it somewhat effective, and 8% found it somewhat ineffective.
Research suggests that intermittent fasting can aid in weight loss and improve insulin sensitivityi XThe sensitiveness of your body cells in response to the insulin hormone in the context of regulating blood sugar levels. and heart health, among other things (1), (2), (3), (4). However, it’s important to remember that intermittent fasting may not be suitable for everyone. Always consult a doctor or nutritionist before starting any new diet or exercise regimen.
2. Anti-inflammatory Diet
An anti-inflammatory diet includes foods believed to help reduce inflammation in the body. Fruits and vegetables high in antioxidants and polyphenols, such as berries, leafy greens, and tomatoes, may help reduce inflammation in the body (5), (6), (7).
Whole grains, chicken, fish, and plant-based options like beans, lentils, and nuts are also believed to be anti-inflammatory. Omega-3 fatty acids found in fatty fish like salmon, sardines, and mackerel, walnuts, and flaxseeds have also been shown to have anti-inflammatory properties (8), (9), (10), (11).
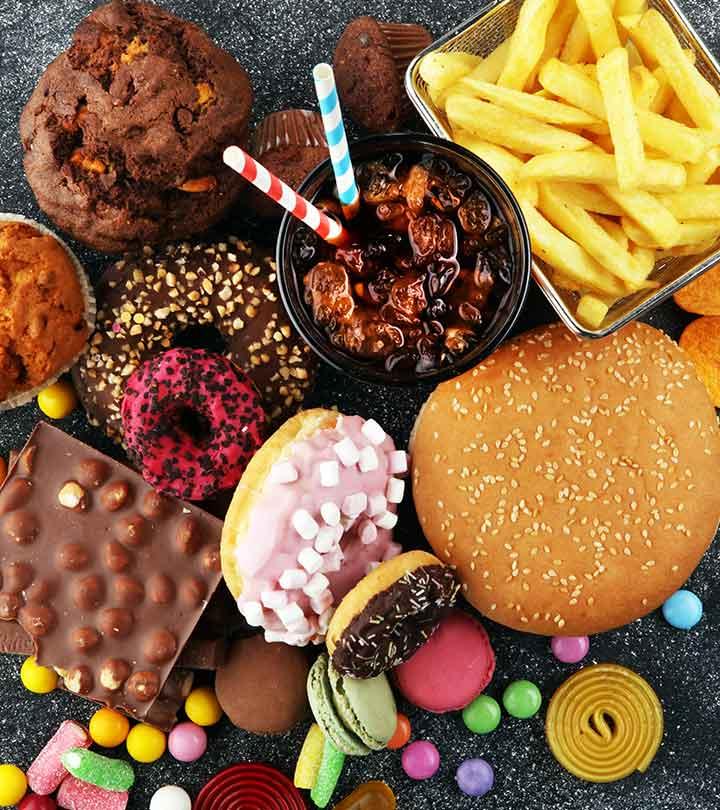
On the other hand, certain foods that cause inflammation are generally avoided on this diet. These include processed foods, fried foods, and foods high in sugar, salt, and saturated fats such as fast foods, snacks, and sweets. Some people may also need to limit foods like gluten and dairy as they may cause gut inflammation (12), (13), (14).
Remember that an anti-inflammatory diet is not a ‘one-size-fits-all’ approach. Always consult a doctor or nutritionist before making any drastic changes to your diet.
3. Fuel Refocus
The diet focuses on high-fat, high-protein, and low-carb food preferences. It emphasizes on consuming fats and protein while restricting carbohydrate intake. This causes the body to enter a metabolic state called ketosis where it burns fat instead of carbohydrates for fuel (15).
On a high-fat, low-carb diet, people typically obtain around 55-60% of their calories from fats, 30-35% from proteins, and 5-10% from carbohydrates. This diet comprises fat intake higher than the typical Western diet (where one gets only around 20-35% of their calories from fat) (15), (16).
It is crucial to remember that people on a very low-carbohydrate ketogenic diet (VLCKD) significantly increased their levels of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) compared to those on a low-fat diet (LFD) (17).
Thus, this diet may not suit all and must be supervised by a medical professional, especially for those with a history of heart disease, diabetes, or metabolic disorders.
These three pillars of this diet, when combined, work towards reducing unwanted weight gain. Does this mean the diet is good for you? Keep scrolling to learn more.
Is The Galveston Diet Good For You?

Menopause is often associated with several physical and psychological changes, including fluctuations in weight. This can be attributed to hormonal imbalances as the body ages and enters menopause (18).
Understanding how these changes affect metabolism and influence weight gain or loss during this transitional period is essential. While some women experience weight gain due to slower metabolism and declining estrogen levels, others may lose weight due to reduced appetite or calorie intake (18).
Learning about the effects of menopause on your body will help you take control of your health – whether it is managing food portions, controlling stress levels, or incorporating regular exercise into your routine.
 Quick Tip
Quick TipThe Galveston diet aims to address the hormonal imbalances solely through nutrition. It was thoughtfully created to regulate weight fluctuations. Learn more about the additional advantages of this diet.
Benefits Of The Galveston Diet
1. May Help Reduce Weight
Several studies have noted the beneficial effects of intermittent fasting on weight management. It can reduce 0.8% to 13% of body weight and decrease your body mass indexi XA health screening tool that calculates the height-to-weight ratio to determine how much body fat you possess. by an average of 4.3%. No severe side effects, besides hunger pangs, were reported (19).
While water loss contributes to the initial weight loss observed on a low-carb diet, true fat reduction happens when one adheres to this type of diet in the long term (20).
2. May Reduce Chronic Inflammation
Inflammation is your immune system’s natural response to injury or infection. However, chronic inflammation has been linked to several health conditions like diabetes, heart disease, and certain types of cancer (21).
Intermittent fasting lowers inflammatory signals and prevents the clogging of blood vessels. This lowers the risk of several cardiovascular disorders (22). Additionally, studies suggest that low-carb diets may help reduce inflammation and alleviate conditions like Parkinson'si XA condition that worsens with time and affects the neurological system and the body, resulting in tremors and stiffness. , multiple sclerosisi XA condition when the immune system attacks the nerves' protective layer and results in vision loss or poor movement. , and fatty liver diseasei XA liver condition brought on by an accumulation of extra fat that results in abdominal pain, weight loss, and fatigue. (23), (24).
3. May Help Control Blood Sugar

Some studies suggest that adopting a very low-carbohydrate ketogenic diet and changing one’s lifestyle can improve the health of people who are overweight and have type 2 diabetes (25), (26). However, not all results were conclusive as some subjects showed insulin resistancei XInadequate response to insulin and inability to absorb glucose from the blood, which results in high blood sugar levels. while others improved their sensitivity towards the hormone via this diet (27). Hence, further long-term studies are warranted in this regard.
4. Does Not Count Calories
Counting calories can cause stress when you are trying to stick to a strict calorie limit. But avoiding it can reduce stress and improve your overall well-being. Rather than focusing on the number of calories you consume, you can focus on the nutritional value of the food.
Rigidly counting calories can lead to disordered eating patterns like binge eating, restriction, and obsession. Focusing on food quality instead of quantity can reduce the risk of disordered eating.
Not counting calories doesn’t mean you should ignore the energy balance of what you are eating. Instead, focus on nutrient-dense and satisfying foods and allow yourself the occasional treat. Keep reading to learn more about the foods you can have on this diet.
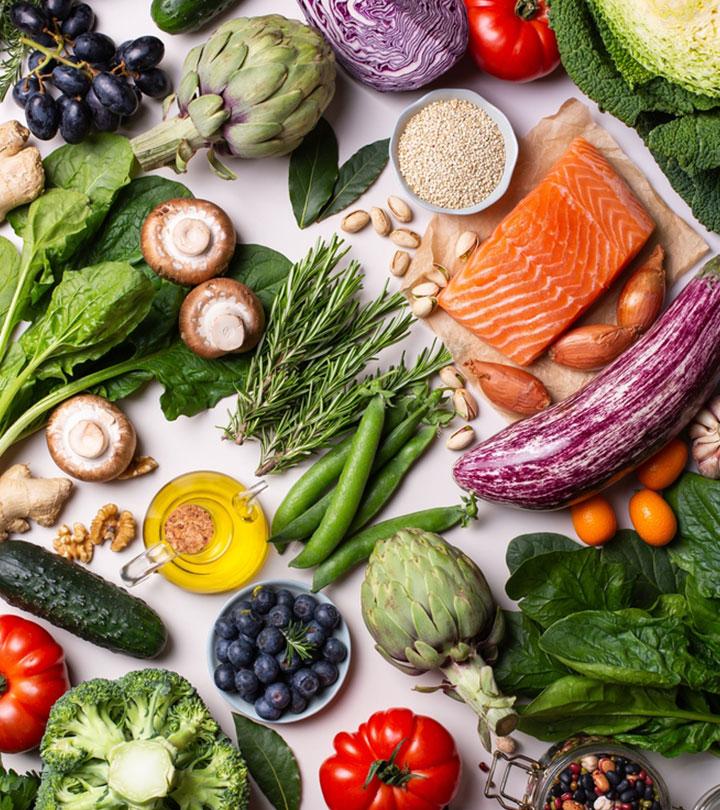
Galveston Diet Food List
The Galveston diet advises high-fat, low-carb, antioxidant-rich, and anti-inflammatory foods. Probiotic-rich fermented foods like kefir, kombucha, and kimchi are also encouraged. You can replace a cup of coffee with herbal teas like oolong or green tea or lime water, which are packed with antioxidants.
This diet advocates against eating pro-inflammatory and nutritionally deficient meals as they can lead to weight gain. A low-carb diet dictates that you restrict your intake of starchy foods like corn, potatoes, beets, etc. Avoid most processed foods, added sugars, and alcohol. However, an occasional glass of red wine is permitted.
Here is a quick look at what foods are allowed and restricted on the Galveston diet:
| What To Eat | What To Avoid |
| Healthy fats (butter, olive oil, coconut oil, sesame oil) | Processed meats (bacon, salami, sausage) |
| Lean protein (chicken, fish, turkey, eggs) | Sweeteners (high fructose corn syrup and added sugars) |
| Fruits (berries) | Refined flour and grains (white bread) |
| Vegetables (broccoli, spinach, kale, cabbage) | Food additives (artificial flavors, colors, preservatives) |
| Whole grains | Vegetable oils (canola oil) |
| Full-fat dairy (cheese, yogurt, milk) | Alcohol |
| Nuts and seeds (peanuts, almonds, pumpkin seeds, chia seeds, sunflower seeds) | Sweetened beverages |
| Legumes | Fried foods |
The diet also promotes replacing high-carb meals with low-carb alternatives. This includes swapping bread with a lettuce wrap, chips with cheese crisps, pasta with zoodles, and mashed potatoes with mashed cauliflower.
 Quick Tip
Quick TipCheck out the sample Galveston diet menu plan below for more ideas on what to eat. It will help you effectively organize your meals while following this diet.
Galveston Diet Meal Plan
The Galveston diet follows the 16/8 intermittent fasting schedule. It is advisable to proceed slowly because the abrupt time-bound restriction on your food intake could be an issue. Start by adhering to the 8-hour diet every other day.
Create a timetable that suits your lifestyle and plan your meals based on your hunger pangs. You only have an 8-hour window to eat, so you must plan well and prepare ahead of time to eat comfortably and well.
Here is an example of a Galveston diet meal plan that can get you started. You can get ideas for your upcoming meals and improve some of the suggested delicacies by adjusting them to your preferences and dietary requirements.
| Meal | What To Eat |
| Breakfast | You can pick one from the options listed below:
|
| Lunch | You can pick one from the options listed below:
|
| Dinner | You can pick one from the options listed below:
|
| Snacks | You can pick one from the options listed below:
|
 Quick Tip
Quick TipScroll down to check some of the simplest and tastiest supper dish recipes you can follow and enjoy on the Galveston diet.
Galveston Diet Recipes
1. Lemon Chicken Quinoa Salad
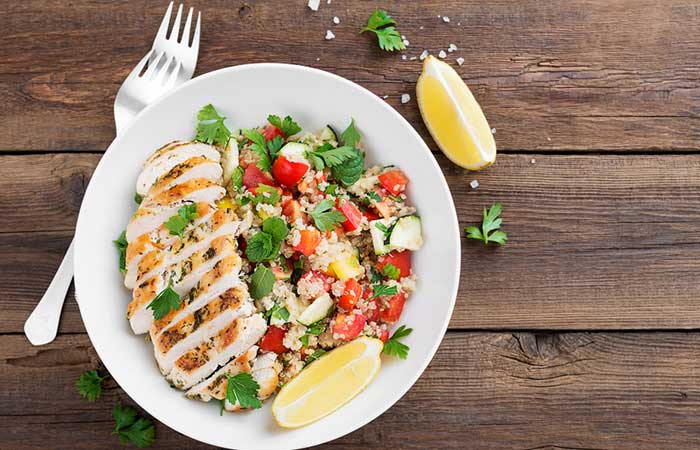

What You Need
- 1 cup quinoa
- 4 chicken breasts
- 9 oz. cherry tomatoes
- 2 cucumbers
- 3 cloves garlic
- ¾ cup lemon juice
- 2 ½ cups chopped parsley
- 2 ½ cups green beans
Instructions
- Mix 1 cup of quinoa with 2 cups of water in a saucepan over medium heat.
- Bring to a boil and turn down the heat.
- Cover and cook until the water is absorbed. Set aside.
- Halve the chicken breast, crush the garlic cloves, and coarsely chop parsley.
- Mix these ingredients with ½ cup of lemon juice and marinate for 15 mins.
- Cook the chicken in a pan over high heat.
- Chop the cucumbers and quarter the tomatoes.
- Mix these ingredients with the leftover lemon juice and add to the cooked quinoa.
- Serve the salad with the chicken and steamed green beans on the side.
2. Scrambled Tofu
What You Need
- 6 oz. firm tofu
- ¼ cup diced onion
- 2 cloves garlic
- 1 tablespoon olive oil
- ¼ cup nutritional yeast
- 1 teaspoon lemon juice
- ¼ teaspoon salt
- ¼ teaspoon pepper
Instructions
- Heat olive oil in a skillet over medium heat.
- Dice the onion and mince the garlic cloves.
- Add them to the skillet and cook until golden brown.
- Add the rest of the ingredients except the tofu and stir.
- Crumble the tofu and simmer for 2-3 mins.
- Adjust the seasonings to your preference and serve.
The Galveston diet may be the secret to many people’s successful weight loss. However, every coin has a flip side. Despite being specifically created for women going through menopause, not all of them may benefit from the diet. Learn if this diet is suitable for you in the next section.
Side Effects Of The Galveston Diet
While this diet may promote weight loss and improve blood sugar control, it can also have some adverse effects.
Some of the common side effects of a high-fat, low-carb diet include (15),(16):
- Fatigue and weakness as the body struggles to adapt to using fat as a primary source of fuel instead of carbohydrates.
- Constipation and other digestive problems due to a low intake of fibrous carbohydrates.
- A fruity or metallic breath caused as a by-product of fat metabolism.
- An increased risk of nutritional deficiencies, as a low-carb diet can miss out on important nutrients found in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
Other potential side effects may include (15),(16):
- Elevated cholesterol levels, particularly in people with a genetic predisposition to high cholesterol.
- Decreased athletic performance due to lowered intake of carbohydrates.
- An increased risk of kidney stones in susceptible individuals due to high fat intake.
The diet’s restriction on certain foods may result in deficiencies in essential nutrients that may have to be balanced with supplements. Intermittent fasting may not be appropriate for people with diabetes and pregnant and breastfeeding women. Additionally, some people may experience side effects such as headaches or hunger during fasting (19).
These side effects usually improve or disappear after a few weeks into the diet, as the body adapts to the changes. Consult a health care professional before starting any new, restrictive diet. Ensure you are getting enough nutrients, especially if you plan to follow the diet for a long period.
Infographic: A Simple Guide To The Galveston Diet
The Galveston diet strikes a balance between intermittent fasting, a high-fat, low-carb diet, and a good serving of anti-inflammatory foods. It is a restrictive diet, so you must keep a close eye on what you eat. Check out the infographic below to learn more about the foods you can include and foods you must away from in the Galveston diet
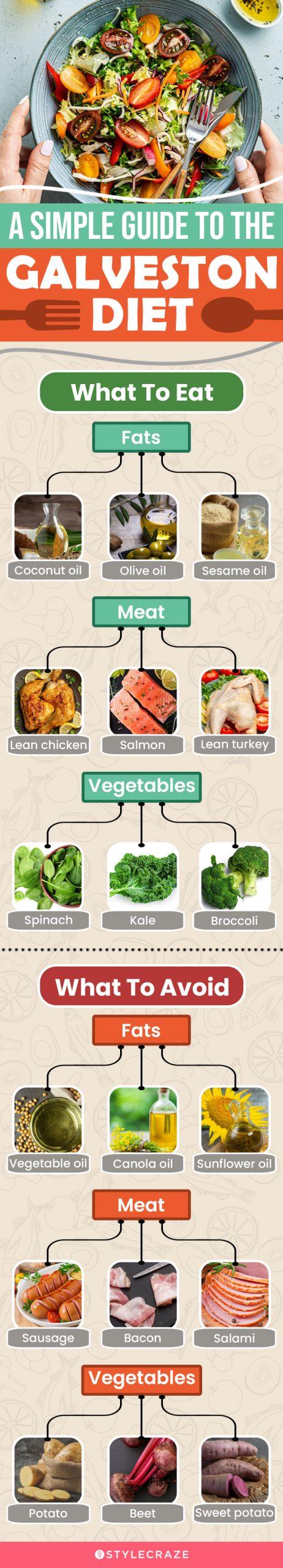
Illustration: StyleCraze Design Team
The Final Word
The Galveston diet is based on a 16/8 intermittent fasting schedule and consists of high-fat, low-carb, anti-inflammatory foods. Proponents claim that this diet can aid in weight loss and improve blood sugar levels. However, there is limited research on the long-term effectiveness and safety of this diet.
That said, this is not a fad diet but a holistic approach to a better life. It should be treated as a lifestyle change and not a short-term solution, only then it may cater to your health and wellness needs. Always opt for a well-balanced diet and exercise routine designed by a nutritionist especially for your body type and lifestyle to achieve sustainable weight loss.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is Galveston diet the same as keto’s?
No, it isn’t. While both diets focus on a high-fat, low-carb diet, the Galveston diet includes a very low-carb diet loaded with anti-inflammatory meals eaten within an 8-hour period.
Is Galveston a laxative?
No, the diet focuses on reducing weight via balancing your hormonal levels rather than boosting bowel movements.
Is the Galveston diet better than the Mediterranean diet?
There is no conclusive evidence suggesting that the Galveston diet is better than the Mediterranean diet. Both diets follow a similar principle of including anti-inflammatory foods. However, the former also includes 16/8 intermittent fasting and is slightly more restrictive.
Key Takeaways
- The Galveston diet is a specific eating regimen designed to help menopausal women lose their unwanted weight gain.
- It is based on 3 primary principles: 16/8 intermittent fasting, a high-fat low-carb diet, and the inclusion of anti-inflammatory foods.
- It is a restrictive diet that aims to alleviate the hormonal imbalances brought on by menopause, thereby addressing the weight gain at its root cause.
- But consult your nutritionist first to confirm if you are the right candidate for this diet and if your blood sugar levels permit you to follow this diet.

Image: Stable Diffusion/StyleCraze Design Team
Learn about the signs and symptoms of perimenopause with the ‘Galveston’ Diet. Get tips from this informative video on how to manage the changes in your body and life.
Personal Experience: Source
StyleCraze's articles are interwoven with authentic personal narratives that provide depth and resonance to our content. Below are the sources of the personal accounts referenced in this article.
i. Say Goodbye to those Darn Menopausal Pounds!https://ceoofmylife.medium.com/say-goodbye-to-those-darn-menopausal-pounds-10a0321b9d16
References
Articles on StyleCraze are backed by verified information from peer-reviewed and academic research papers, reputed organizations, research institutions, and medical associations to ensure accuracy and relevance. Read our editorial policy to learn more.
- Intermittent Fasting and Metabolic Health
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8839325/ - Cardiometabolic Benefits of Intermittent Fasting
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34633860/ - Intermittent Fasting: Is the Wait Worth the Weight?
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5959807/ - INTERMITTENT FASTING AND HUMAN METABOLIC HEALTH
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4516560/ - Berries as a Treatment for Obesity-Induced Inflammation: Evidence from Preclinical Models
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7912458/ - In Vitro Anti-Inflammatory Properties of Selected Green Leafy Vegetables
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6316011/ - Enhancing the Health-Promoting Effects of Tomato Fruit for Biofortified Food
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3972926/ - Whole Grain Consumption and Inflammatory Markers: A Systematic Literature Review of Randomized Control Trials
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8778110/ - Chicken Protein Hydrolysates Have Anti-Inflammatory Effects on High-Fat Diet Induced Obesity in Mice
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6473722/ - Potential anti-inflammatory effects of legumes: a review
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35042569/ - Omega-3 fatty acids and inflammatory processes: from molecules to man
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28900017/ - A proinflammatory diet is associated with inflammatory gene expression among healthy
non-obese adults: Can social ties protect against the risks? - Pro-inflammatory diet is associated with a high number of cardiovascular events and ultra-processed foods consumption in patients in secondary care
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33148359/ - Proinflammatory Dietary Intake is Associated with Increased Risk of Metabolic Syndrome and Its Components: Results from the Population-Based Prospective Study
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7230546/ - Ketogenic Diet
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK499830/ - Long-term effects of a ketogenic diet in obese patients
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2716748/ - Advantages and Disadvantages of the Ketogenic Diet: A Review Article
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7480775/ - Menopause
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK507826/ - Intermittent fasting and weight loss
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7021351/ - Low Carbohydrate Diet
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK537084/ - Chronic inflammation in the etiology of disease across the life span
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7147972/ - Intermittent Fasting in Cardiovascular Disorders—An Overview
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6471315/ - Ketogenic diet and Neuroinflammation
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32987244/ - Effect of a ketogenic diet on hepatic steatosis and hepatic mitochondrial metabolism in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7132133/ - An Online Intervention Comparing a Very Low-Carbohydrate Ketogenic Diet and Lifestyle Recommendations Versus a Plate Method Diet in Overweight Individuals With Type 2 Diabetes: A Randomized Controlled Trial
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5329646/ - Implementing a low-carbohydrate ketogenic diet to manage type 2 diabetes mellitus
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30289048/ - Effects of Ketogenic Diets on Cardiovascular Risk Factors: Evidence from Animal and Human Studies
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5452247/




























