24 Health Benefits Of Potatoes, Types, And Recipes
Heck, yes! Everyone's favorite vegetable is also good for your health!

Image: Shutterstock
Potatoes (Solanum tuberosum) are a staple worldwide and a favorite for most individuals. However, many people often doubt the benefits of potato, given all the negative talk surrounding this affordable, starchy vegetable. But, what does science say? This article makes it clear to you how potato benefits your health besides discussing their nutritional profile, delicious recipes to make at home, and more. Keep reading.
 Know Your Ingredient: Potato
Know Your Ingredient: PotatoWhat Is It?
A starchy, perennial vegetable full of essential nutrients, such as vitamin C and potassium.
What Are Its Benefits?
It lowers blood pressure, improves heart and brain health, increases collagen production, and prevents hair loss.
Who Can Use It?
All except people who are on a low-glycemic or low-carbohydrate diet.
How Often?
It can be consumed daily and applied topically twice a week.
Caution
People with latex or pollen allergies should avoid using raw potatoes on their skin.
In This Article
What Are The Different Types Of Potatoes?
Russet – These are the classic potatoes. They are ideal for baking and are also good fried and mashed.
Fingerling – These are finger-shaped and small and stubby. They naturally grow narrow and small.
Red – They have a waxy texture, which is why their flesh stays firm throughout the entire cooking process. They have thin yet vibrant red skins.
White – They hold their shape well even after cooking. They make a great addition to salads as their delicate and thin skins add the right amount of texture.
Yellow – They have golden skin and yellow to golden flesh. Grilling them gives them a crispy skin that enhances the dense flesh.
Purple – They have moist and firm flesh and add a vibrant color to salads. The purple color of this type of potatoes is preserved best by microwaving.
And wait, they do have an interesting history.
What Is The History Of Potatoes?
Potatoes were first domesticated between 8000 and 5000 BC in modern-day Peru and northwestern Bolivia. The introduction of potatoes was responsible for over a quarter of the growth in Old World population and urbanization from 1700 to 1900.
But the lack of genetic diversity left the potato crop vulnerable to disease. In 1845, a plant disease known as late blight spread through Western Ireland and parts of the Scottish Highlands – resulting in crop failures that caused the Great Irish Famine.
And well, as of 2014, the world’s production of potatoes had crossed 380 million tonnes.
It’s no wonder potatoes are so popular and loved by all. According to USDA’s Economic Research Service, potatoes are the top vegetable choice for Americans. US residents consumed an average of 156.3 pounds of vegetables per person in 2015. Out of these, potatoes bagged the number one spot at 48.3 pounds of potatoes per person, which included fresh potatoes, canned potatoes, and potato chips.
 Trivia
TriviaWhat About The Nutritional Value Of Potatoes?
| NUTRITION FACTSSERVING SIZE 369G | ||
|---|---|---|
| Amount Per Serving | ||
| Amount Per Serving | Calories from Fat 3 | |
| % Daily Value* | ||
| Total Fat 0g | 1% | |
| Saturated Fat 0g | 0% | |
| Trans Fat | ||
| Cholesterol 0mg | 0% | |
| Sodium 22mg | 1% | |
| Total Carbohydrate 68g | 23% | |
| Dietary Fiber 8g | 32% | |
| Sugars 3g | ||
| Protein 7g | ||
| Vitamin A | 0% | |
| Vitamin C | 121% | |
| Calcium | 4% | |
| Iron | 16% | |
| VITAMINS | ||
| Amounts Per Selected Serving | %DV | |
| Vitamin A | 7.4IU | 0% |
| Vitamin C | 72.7mg | 121% |
| Vitamin D | – | – |
| Vitamin E (Alpha Tocopherol) | 0.0mg | 0% |
| Vitamin K | 7.0mcg | 9% |
| Thiamin | 0.3mg | 20% |
| Riboflavin | 0.1mg | 7% |
| Niacin | 3.9mg | 19% |
| Vitamin B6 | 1.1mg | 54% |
| Folate | 59.0mcg | 15% |
| Vitamin B12 | 0.0mcg | 0% |
| Pantothenic Acid | Ir1.1mgon | 11% |
| Choline | 44.6mg | |
| Betaine | 0.7mg | |
| MINERALS | ||
| Amounts Per Selected Serving | %DV | |
| Calcium | 44.3mg | 4% |
| Iron | 2.9mg | 16% |
| Magnesium | 84.9mg | 21% |
| Phosphorus | 210mg | 21% |
| Potassium | 1554mg | 44% |
| Sodium | 22.1mg | 1% |
| Zinc | 1.1mg | 7% |
| Copper | 0.4mg | 20% |
| Manganese | 0.6mg | 28% |
| Selenium | 1.1mcg | 2% |
| Fluoride | – | |
The benefits of potato are far and wide due to its nutrient content and one small potato contains about 30 grams of carbohydrates. And one cup of mashed potatoes contains about 214 calories. One small baked potato contains 129 calories, and so does one small roasted potato.
If you are wondering…
Potato has as wide a range of benefits as the nutrients it contains.
What Are The Health Benefits Of Potatoes?
Potatoes are rich in fiber and potassium, which contribute to most of its benefits. They help lower blood pressure and protect the heart and even treat inflammation and the resultant diseases like cancer and rheumatismi XA medical condition that causes tender swollen joints, fatigue, and joint stiffness when the immune system attacks healthy body tissue. .
1. Lower Blood Pressure
Research has revealed that the skin of potatoes is rich in potassium – a mineral that can help lower blood pressure. An average-sized baked potato has about 535 mg of potassium (and just 17.3 mg of sodium), which is roughly about 15 percent of the daily recommended amount. High levels of potassium in the blood can make the kidneys excrete more salt and water – and this helps reduce blood pressure (1).
In fact, taking potassium is just like taking a diuretic. Potassium was also found to help the heart function optimally and help the nerves and muscles communicate.
Another study states that eating a portion of potato twice a day can help lower blood pressure (2). Baked and boiled potatoes are also acceptable. Research also has shown that potatoes contain certain plant chemicals similar to those found in blood pressure medication.
But it is important to note that all of this depends on the way potatoes are prepared. The healthiest way to eat potatoes is to first cook them in a microwave oven with no oil, fat, etc. Also, deep frying is a no-no as the process subjects the vegetable to high temperatures that destroy the nutrients present in it.
However, we want you to consult your doctor before you make this vegetable a regular part of your diet (if you have issues with hypertension, that is). Because one study states that the effect of potatoes on hypertension is unclear – they could be high in potassium, but they are also high in glycemic carbohydratesi XThey are indicated by the glycemic index that ranks carbohydrates based on how quickly or slowly they can increase the blood sugar level. (2).
2. Improve Heart Health
Potatoes don’t contain cholesterol, which is good news. And they contain fiber, potassium, vitamins C, and vitamin B6 – all of which are great for heart health. The fiber in the vegetable helps lower excess cholesterol levels in the blood. And potassium protects the heart too – one study concluded by stating that consuming 4,069 mg of potassium in a day can cut the risk of ischemic heart disease by 49 percent.
From studies, consuming more fiber (potatoes especially) can lower the risk of heart disease (3). But potatoes are also high in glycemic index, and this could be a negative aspect when it comes to heart health. And though potatoes contain complex carbohydrates (fiber), those found in whole grains are preferred to those in starch-heavy foods like potatoes (4).
3. Prevent Cancer
Studies have revealed that eating potatoes won’t cause cancer, unless you eat them fried. So, if you have been under the impression that potatoes might cause cancer, well, you can relax. Boiling, mashing, or even baking potatoes could make them far more beneficial. Frying potatoes can lead to the synthesis of a chemical called acrylamide, which causes cancer (5).
In addition to not causing cancer, potatoes can even cut cancer risk – as per a study. And this can be attributed to the vitamin C content in potatoes. Women who consume more than 60 mg/day of vitamin C when compared with women who are not taking any supplements had a 30% reduced risk of colorectal cancer (6).
Baked purple potatoes were also found to cut colon cancer risk. Researchers had observed that extracts of baked potatoes hinder the spread of colon cancer stem cells – and even totally destroyed them in some cases.
4. Improve Brain Health
Potatoes also contain alpha lipoic acid, a coenzyme that contributes to brain health. The acid had shown to improve memory deficits in Alzheimer’s and even had reduced cognitive decline in certain patients (7).
Potatoes were also found to aid in depression treatment. They can affect the neurotransmitters in the brain that are responsible for managing mood levels – and interestingly, these are the same neurotransmitters targeted by medication. Eating one plain potato before you go to bed can help your body regulate your emotions and moods. But guess what – just ensure potatoes aren’t the only thing you eat.
The vitamin C in potatoes also has a role to play in treating depression. The vitamin is an antioxidant, and it helps prevent cell damage – especially in the brain (8).
5. Promote Stronger Bones
As per the University of Maryland Medical Center, the magnesium and potassium in potatoes can contribute to bone health. The two minerals can help prevent bone loss in both men and women (9).
6. Reduce Inflammation
According to Arthritis Foundation, yellow and purple potatoes can reduce inflammation (10). This could also mean protection against arthritis and rheumatism.
As per another study, the glycoalkaloids in potatoes (the bitter compounds in the vegetable) and potato peel extracts exhibit anti-inflammatory effects. The study, however, states the necessity for further investigation before the vegetable can be used for therapeutic purposes (11). Potatoes also contain compounds called anthocyanins that also offer anti-inflammatory benefits. They are particularly effective in treating gut inflammation. Potatoes also suppress oxidative stress and gut inflammation in murine colitis (colitis in mice) (12).
According to another American study, potato consumption can alter inflammatory damage in men (13).
7. Promote Digestion
The large amount of carbohydrates in potatoes help fuel the reactions in the body required for different processes, one of them being digestion (14). And coming to fiber – one singled baked potato offers you 12 percent of the RDA. Fiber supports digestion and promotes regularity. Most of the fiber in potatoes is found in the skin. And the starch in the potato also adds bulk to the stool – as it is indigestible.
Potatoes can also keep diarrhea away. Consuming calories and carbohydrates during diarrhea can help revive the energy levels pretty quick. This can accelerate recovery. Potatoes are also rich in potassium, a mineral one loses to a large extent during diarrhea. And as potatoes are bland, they are far less likely to aggravate your symptoms as compared to fatty or spicy foods.
But by potatoes, we only mean baked or boiled or mashed variants, and not potato chips or fries – they only make things worse. And guess what – one bag of potato chips contains about 120 grams of carbs.
8. Enhance Immunity
Research suggests that pigmented potatoes can also have beneficial effects on the immune system (15). Studies have found that consuming potatoes might decrease leukocytesi XWhite blood cells that are part of the immune system. They are made in the bone marrow and protect the body against various infections. , which are produced in the human body due to inflammation or when a person is ill.
9. Aid In Weight Management
A plain potato is an extremely satiating vegetable – it keeps you full for long periods. So if you are trying to lose weight, this helps. And worry not – you don’t have to always eat potatoes plain to keep your weight in check. You can also top a baked white potato with some steamed broccoli and sprinkle some low-fat cheese on it – this can act as a filling and delicious lunch.
According to a study, potatoes can inhibit food intake. The protease inhibitors concentrate extracted from potatoes was found to reduce food intake and weight gain (16).
And on the other hand, potatoes can also lead to healthy weight gain. Since the vegetables have a caloric value, consuming them in normal amounts can lead to a sustained and healthy weight gain.
10. Help Lower Blood Cholesterol
The cholesterol-lowering properties of potatoes come from their fiber content. The vegetable is a good source of both soluble and insoluble fiber – and the former helps lower bad cholesterol (17). It is important to note that most of the beneficial fiber of a potato lies in its skin – and removing that simply means removing the fiber. Also, potatoes by themselves can reduce cholesterol – provided you don’t fry them or add stuff that contributes to cholesterol. Baking your potatoes and adding some olive oil on the top can make a great snack.
11. Alleviate Premenstrual Symptoms
Drinking potato juice can help relieve PMS symptoms according to a study. The carbohydrates in the juice can help elevate the levels of tryptophan, an amino acid that boosts serotonin production. Serotonin is responsible for improving mood and reducing anxiety (18).
12. Promote Sleep
The potassium in potatoes acts as a muscle relaxant, which aids better sleep.
13. Help Treat Scurvy
Since potatoes are good sources of vitamin C, they sure can aid in the treatment of scurvy (19).
14. Treat Kidney Stones
Eating potatoes (given they are rich in fiber) may improve overall health and prevent the recurrence of kidney stones. And since potatoes are also rich in magnesium (and low in calcium, the excess of which can also lead to kidney stones), they can play a role in preventing kidney stones. However, limited research is available in this regard.
What Are The Benefits For The Skin?
The potato peel, and even the potato juice, can greatly improve your skin health. A potato facial or face mask helps treat acne and other skin conditions like dark spots and blemishes. The vegetable also works equally well for skin whitening.
15. Remove Dark Circles
Applying potato under the eyes helps banish those under eye dark circles. And this is how you do it.
- Peel a raw potato and slice it into large, even pieces.
- Wrap them in a clean cloth and place it over your dark circles for about 20 minutes. Gently wash your eyes with warm water.
This procedure can also help you get rid of puffy eyes.
16. Treat Wrinkles
Potato works effectively well in slowing down the signs of aging, especially wrinkles. The antioxidants in the vegetable, like vitamin C, can do the job.
Applying potato paste on the face can do wonders. Just peel and mash potatoes and apply the paste on your skin. Leave it on for about 20 minutes and then wash with cold water.
17. Eliminate Dark Spots
Potatoes can help eliminate dark spots as well. This is how you can use them:
- Blend peeled potatoes in a blender.
- Apply the paste on your face. Gently massage for about 5 minutes.
- Wash your face with clean and cold water.
- Repeat this every day for best results.
You can also use potatoes for removing blemishes and pimples. Simply use potato juice as a daily facial rinse. The remedy might also help treat pimples.
Using potatoes as a cleanser can also help remove dark spots and other impurities on the skin. It works well for oily skin too. For this purpose, you need a cucumber and a potato.
- Cut the two into medium pieces and blend them for about 20 seconds.
- Add 1 teaspoon of baking soda and some water to this mixture. Use it to clean your face – post which you can rinse with regular water.
18. Treat Sunburns
The vegetable works well to treat sunburns. Just place cold potato slices on the affected areas of your skin. Leave them on for about 20 minutes and remove. You can also dab potato juice on the spot. Doing so gives you a cooling sensation and even diminishes your suntan.
19. Help Lighten Skin
Did you know that potatoes are a natural skin lightening agent? This is what you can do with the vegetable:
- Grate a raw potato and apply the mask on your face. Rinse with water after 30 minutes.
- Using this regularly can make your face clean and bright.
You can also use the juices of potato and lemon to lighten your skin naturally. The potato lemon mask can act as a mild bleach and do the job well.
20. Treat Dry Skin
If you have dry skin, all you need to do is turn to your kitchen. And pick one potato and half a teaspoon of curd.
- Grate the potato and mix it with the curd.
- Apply the paste on your face and leave it on for 20 minutes.
- Wash with regular water.
This mask replenishes skin moisture and treats dry skin.
21. Exfoliate Skin (Remove Dead Skin Cells)
Simply apply grated and peeled potatoes on your face and leave on for 10 minutes. Rinse with clean water. Doing this regularly can help remove dead skin cells and rejuvenate your skin.
22. Improve Collagen Health
We already saw that potatoes are rich in vitamin C. And vitamin C builds collagen. Having potatoes regularly (in a healthy way, of course) can help improve collagen health.
What Are The Benefits Of Potatoes For The Hair?
Potatoes have important benefits for the hair as well. They help slow down premature graying of hair and even prevent hair loss – both conditions that can even affect one’s self-esteem.
23. Help Treat Gray Hair
A potato hair tonic can do wonders for your hair and prevent and even treat premature graying. This is how you prepare it:
- Boil potato peels in a pan of water. The level of water should just be enough to cover the peels.
- After boiling, strain the water into a tumbler.
- Use this water to rinse your hair after shampooing. This can restore the natural color of your hair.
Following this for every alternate hair wash can get you good results. This is one of the uses of potato peel. For this purpose, you can also use normally boiled potato water if you are preparing any dish using the vegetable.
24. Prevent Hair Loss
A hair mask consisting of potato and honey can help prevent hair loss. And this is the procedure –
- Peel the potato and extract the juice.
- Mix 2 tablespoons of this potato juice with 2 tablespoons of aloe vera and 1 tablespoon of honey.
- Apply this mixture to the roots and massage your scalp.
- Cover your hair with a shower cap and leave it on for a couple of hours.
- Wash your hair with a mild shampoo.
You can apply this mask twice a week for best results.
That’s with the benefits. Now if you are wondering…
How To Incorporate More Potatoes In Your Diet
Most of the nutritious content of a potato is in its skin. Hence, it makes sense to consume the vegetable with its skin on. You can make potatoes a part of your meal by adding them to salads or use mashed potato as a side-dish for your breakfast.
Or…
Potato Recipes?
Potato recipes are both delicious and healthful – given that most individuals like them. A few of the most popular recipes include homemade BBQ chips, roasted rainbow potatoes, and stuffed peppers and potatoes.
1. Roasted Rainbow Potatoes
What You Need
- 2 pounds of rainbow fingerling potatoes, cleaned and halved
- 2 crushed garlic cloves
- 2 tablespoons of extra virgin olive oil
- 1 lemon zest
- 1 tablespoon of finely chopped cilantro
- 1 tablespoon of salt
Directions
- Preheat the oven to 425o F. Line a baking sheet with aluminum foil.
- Clean and halve the potatoes and put them in a bowl. Over these potatoes, add the lemon zest, olive oil, crushed garlic cloves, and salt. Toss.
- Spoon out the potatoes evenly on the lined baking sheet and bake for 15 minutes.
- Remove from oven, turn them over, and bake for 10 more minutes.
- Remove from oven and sprinkle with cilantro.
- Serve.
2. Stuffed Peppers And Potatoes
What You Need
- For the pepper bowl
- 4 bell peppers
- ¼ tablespoon of olive oil
- ½ teaspoon of salt
For the filling
- 3 large shredded potatoes
- 1 shredded yellow onion
- Salt
- 1 teaspoon of ground black pepper
- A few sprinkles of chilli peppers
- 1 tablespoon of olive oil
For the topping
1 tablespoon of sour cream for each half of the pepper
Directions
- Preheat oven to 375o F.
- Wash the peppers and cut them into halves. Remove the seeds.
- Place them in the oven and bake for 10 minutes.
- Add the salt, ground black pepper, chilli peppers, and oil. Mix well.
- Take the peppers out of the oven and stuff them completely with the filling mixture.
- Once done, cover the baking pan with aluminum foil for the first 15 minutes. Remove the foil. Continue baking uncovered at 375o F for about 40 minutes or until the potatoes are done.
- Serve.
The recipes are great. But…
What About The Facts On Potatoes?
- An average human eats about 33 kilograms of potatoes in a year.
- Way back in 1995, potato became the first vegetable to be grown in space.
- The world’s biggest potato weighed about 3.8 kilos.
- China is the leading producer of potatoes in the world.
- Potatoes contain a toxin called solanine, which can reach dangerous levels in green potatoes. In rare cases, they can cause headaches, cramps, and diarrhea.
- Potato consumption around the world grew from 30 million tonnes in the 1960s to 165 million tonnes in 2000s.
 Trivia
TriviaAnd well…
Any Other Uses Of Potatoes?
You can use potatoes to remove stains on the hands. Even rubbing a potato on the face can help you quickly cleanse it.
You can also use potatoes to remove tarnish from silverware. Boil potatoes, keep them aside for further use, and place your silverware in the boiled water. Let it stay for an hour, and then remove and wash them normally.
Restore old shoes using potatoes. Cut potatoes in half and rub them over your old shoes before you apply polish – this will give them a better shine.
Now, we come to the most important part…
How To Select And Store Potatoes
Selection
These days, potatoes are easily available at most retail outlets in the packaged form, inside a plastic bag. But it is always better to buy them individually from a bulk display so that you can properly inspect them for any signs of decay or damage. Moreover, since the plastic bags are not perforated, they can cause a build-up of moisture, which negatively affects the potatoes.
- While buying potatoes, choose the ones that have smooth and firm skin without eyes or discoloration.
- Avoid the potatoes that have wrinkled or wilted skins, soft dark areas, sprouts, cuts, bruises and green tinges.
- Green-tinged potatoes should particularly be avoided as they contain toxic alkaloids such as solanine formed due to exposure to light.
- This alkaloid not only imparts an undesirable taste but also causes a host of health problems such as circulatory and respiratory depression, diarrhea, and headaches.
- Potatoes with sprouts should also be avoided as they are old.
- If you are buying potatoes in a bag, check properly to discard any rotten potato as it can spoil the others.
- Often, stores offer cleaned potatoes that are a bit costlier. However, these should be avoided as their protective coat has been removed by washing, making them more vulnerable to bacteria.
- New potatoes should be preferred for boiling and salads as they have a thinner skin and are firmer.
Storage
Storing the potatoes properly is also equally important.
- As far as storage is concerned, potatoes should be stored in a cool, dark, dry and properly ventilated place at a temperature of 40o F to 45o F. Higher temperatures or even room temperature will cause them to sprout and dehydrate.
- Root cellars are quite appropriate for providing this type of environment.
- Alternatively, potatoes can also be stored in a cool, dark closet or basement.
- They should not be exposed to sunlight as light triggers the formation of toxic solanine.
- They should not be refrigerated as this will cause their starch to get converted into sugar, giving them a sweet taste.
- Moreover, they should not be kept near onions because the gases they emit will cause both the vegetables to go bad.
- Potatoes should be kept in a burlap or paper bag.
- Mature potatoes have a shelf life of 2 months. They should be frequently checked to discard the sprouted or shriveled ones as they might adversely affect the quality of others.
- New potatoes, being more perishable, can be stored up to a week.
- Cooked potatoes can be refrigerated for several days, but it is advisable not to freeze them as they tend to become watery after reheating.
- Potato contains nearly 80% water, which separates from the starch, making the reheated potato dish watery.
Also…
Any Tips For Cooking And Eating?
Potatoes fall under the category of the most delicious and filling vegetables that can match well with any ingredient. Their skins are not only edible but also a great source of dietary fiber. Thus, they can be cooked with their skins to get the most nutrition value from these vegetables. Potatoes have high calories, but they are also quite healthy.
- It is advisable to wash the potatoes just before cooking them.
- They should be scrubbed under cold running water, and any deep eyes and bruises should be removed with a paring knife.
- If you are peeling them, you can do so with a vegetable peeler, removing only a thin layer of skin to retain the nutrients that lie just below the skin.
- Cleaned and cut potatoes should not be exposed to air to avoid discoloration.
- If it is not possible to cook them immediately after cutting, they should be placed in a bowl of cold water to which you have added a little bit of lemon juice.
- This will prevent them from darkening as well as help maintain their shape during cooking.
- Moreover, they should not be cooked in iron or aluminum pots or cut with a carbon steel knife as they are sensitive to certain metals that may cause them to discolor.
 Quick Tip
Quick TipWe saw the great stuff about potatoes. But there also is the not-so-great stuff.
Any Side Effects Of Potatoes?
Damaged or green potatoes or those with sprouts contain harmful chemicals that can lead to headache, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, restlessness, and, in certain cases, even death. The poisonous substances in such potatoes cannot be destroyed by cooking – so, take care.
And though unblemished and ripe potatoes are safe for pregnant women, don’t use potatoes as medicine in this case as we don’t know what might happen.
Infographic: Do Potatoes Contribute To Weight Gain?
Potatoes are versatile starchy vegetables with many health benefits. However, they have got a bad rap for being unhealthy and causing weight gain. Eating potatoes or their products in excess may lead to extra fat mass. But remember that not all types of potatoes increase waist circumference or elevate obesity risk. Eating them in moderation and avoiding other fatty substances to cook these root vegetables will not lead to weight gain. Click on the infographic below to learn more about the link between potatoes and weight gain. Illustration: StyleCraze Design Team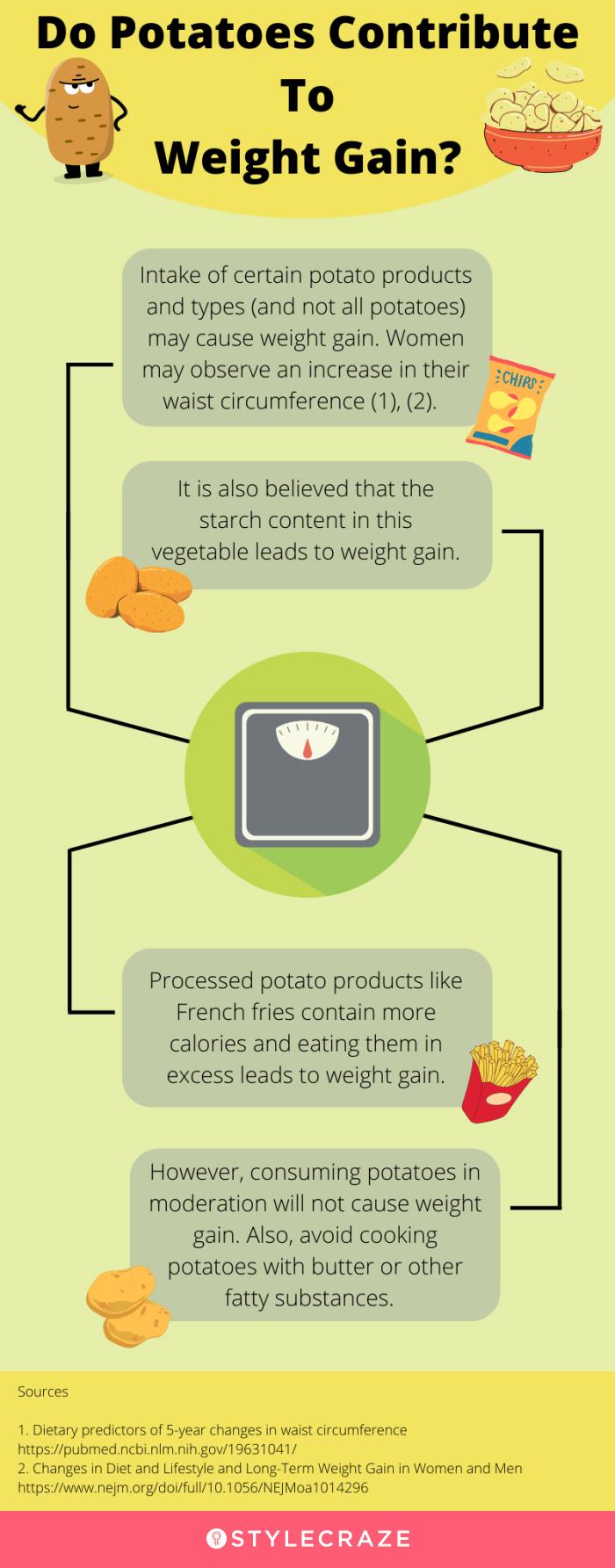
Khyati Jain, a blogger, highlights the nutritional benefits of potatoes, debunking the myth that they cause weight gain. She added, “I have been eating potatoes my whole life. And I have maintained the same weight for the past five years (i).” She touches on a potato-centric diet trend, advises on healthy cooking methods, and cautions against excessive consumption for those with diabetes. Khyati shares her lifelong positive experience with potatoes, encouraging their inclusion in a balanced diet.
Potato benefits you in multiple ways. It can lower blood pressure and improve cardiovascular, brain, bone, digestive, and kidney health. It also may reduce cancer risk and inflammation and promote immunity. In addition, it can boost skin and hair health. However, consuming potatoes with sprouts or those that are green may have negative health effects. Hence, caution is advised. Include potatoes in your routine to reap the benefits they offer. You can try any of the recipes mentioned above to enjoy potatoes in a tasty and healthy form.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can you eat potatoes raw?
Not really. Eating potatoes raw can cause abdominal cramps and fever. Cooking them kills the bacteria.
Can you eat seed potatoes?
There is insufficient information on this. Because seed potatoes are usually not treated to prevent sprouting. Sprouting can make a potato poisonous. So stay safe and avoid use.
Do you lose the nutrients if you peel a potato’s skin?
Yes.
Does the potato diet work?
The potato diet has potatoes, obviously, as the main ingredients. And most often, it can work. Because potatoes can keep you full for long. However, it is better you speak to your health care provider once.
Can you eat potatoes that are still sprouting?
Never.
Is it safe to eat potatoes if they look green?
No.
Is it healthy to eat potatoes daily?
Yes, it is healthy to eat potatoes daily as they are a good source of fiber and help achieve satiety.
Are potatoes healthier than rice?
Yes, potatoes are healthier than rice as they contain more nutrients, are richer in fiber, and are lower in calories than rice.
Is potato better than bread?
Yes, potatoes are higher in fiber and starch than bread. They are also not refined like bread, which makes them healthier. But for bodybuilders who are trying to bulk up, bread is better as potatoes are low calorie compared to bread.
Are potatoes good for diabetes?
No, potatoes have a high glycemic index (GI) and glucose load (GL), which can increase the risk of type 2 diabetes. But sweet potatoes or boiled potatoes can be consumed safely as they have a low GL (20).
Key Takeaways
- Potatoes may help lower cholesterol and blood pressure levels due to their rich fiber and potassium content.
- The juice and peel of a potato help treat many skin conditions, such as acne and dark circles.
- In addition, they help prevent hair loss and promote healthy, strong hair.
- However, the intake of diseased potatoes may cause nausea, vomiting, and headache.

Image: Stable Diffusion/StyleCraze Design Team
Potato is a super veggie that is packed with health benefits! Watch this informative video to learn how to get the most out of it.
Personal Experience: Source
StyleCraze's articles are interwoven with authentic personal narratives that provide depth and resonance to our content. Below are the sources of the personal accounts referenced in this article.
i. I Ate Potatoes Daily For 5+ Years — No, They Don’t Lead to Weight Gainhttps://medium.com/in-fitness-and-in-health/i-ate-potatoes-daily-for-5-years-no-they-dont-lead-to-weight-gain-42ca703c613c
References
Articles on StyleCraze are backed by verified information from peer-reviewed and academic research papers, reputed organizations, research institutions, and medical associations to ensure accuracy and relevance. Read our editorial policy to learn more.
- Effect of potassium intake on blood pressure
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/2104250/ - Potato intake and incidence of hypertension: results from three prospective US cohort studies
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4870381/ - Dietary fibre intake and risk of cardiovascular disease: systematic review and meta-analysis
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3898422/ - Starchy Carbohydrates in a Healthy Diet: The Role of the Humble Potato
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6267054/ - Dietary Acrylamide and the Risks of Developing Cancer: Facts to Ponder
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5835509/ - Vitamin C
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK225480/ - Brain foods: the effects of nutrients on brain function
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2805706/ - Ascorbic Acid and the Brain: Rationale for the Use against Cognitive Decline
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4011065/ - Nutrients and Dietary Patterns Related to Osteoporosis
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7400143/ - Pigmented potato consumption alters oxidative stress and inflammatory damage in men
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21106930/ - Anti-inflammatory properties of potato glycoalkaloids in stimulated Jurkat and Raw 264.7 mouse macrophages
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23454444/ - ANTI-INFLAMMATORY AND ANTI-OXIDANT EFFECTS OF POTATO ANTHOCYANINS — ROLE OF GUT BACTERIA
https://portal.nifa.usda.gov/web/crisprojectpages/1008024-anti-inflammatory-and-anti-oxidant-effects-of-potato-anthocyanins–role-of-gut-bacteria.html - Pigmented potato consumption alters oxidative stress and inflammatory damage in men
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21106930/ - Digestion of polysaccharides of potato in the small intestine of man
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/3812341/ - Golden Sweet Potato as Natural Immunity Booster: A review
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/354370525_Golden_Sweet_Potato_as_Natural_Immunity_Booster_A_review - Potato protease inhibitors inhibit food intake and increase circulating cholecystokinin levels by a trypsin-dependent mechanism
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3033477/ - Potato Fibers Have Positive Effects on Subjective Appetite Sensations in Healthy Men but Not on Fecal Fat Excretion: A Randomized Controlled Single-Blind Crossover Trial
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7697495/ - Serotonin and Mental Disorders: A Concise Review on Molecular Neuroimaging Evidence
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4293164/ - Scurvy in the Great Irish Famine: Evidence of Vitamin C Deficiency From a Mid-19th Century Skeletal Population
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3467765/ - Potatoes Consumption and Risk of Type 2 Diabetes: A Meta-analysis
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6294859
































