14 Health Benefits Of Elderberry, Uses, Dosage, And Recipes
The impressive nutritional profile of these berries can help tackle diabetes, inflammation, and more.

Image: ShutterStock
Elderberry benefits are sure to make you crave a few. These purple berries grow in temperate to subtropical regions. Their antioxidant content contributes to their health benefits. For example, elderberries promote immunity, reduce cancer risk, and protect the heart. These berries are also good for skin and hair. This article discusses the benefits of elderberries, their nutritional profile, their recommended dosage, and their risks. Scroll down.
 Know Your Ingredient: Elderberry
Know Your Ingredient: ElderberryWhat Is It?
A deep red or bluish-black berry of the Elderberry tree that has a tart or acidic taste.
What Are Its Benefits?
It may boost immunity, support proper digestion, maintain blood pressure, and promote eye health.
Who Can Consume It?
Anybody can consume this except people on chemotherapy, diuretics, and immunosuppressant medication.
How Often?
You can consume up to 2 elderberries daily.
Caution
Avoid consuming elderberries if you are pregnant or breastfeeding. Excess consumption may lead to nausea and diarrhea
In This Article
What Are Elderberries?
Scientifically called Sambucus berries, elderberries (also called elderflower) belong to a genus of flowering plants in the family Adoxaceae. The fruit is found in temperate to subtropical regions in the world. The elderberry tree is more widespread in the Northern Hemisphere, while in the Southern Hemisphere, it is found in parts of Australasia and South America. Several species of elderberries are cultivated not just for the fruit, but also for their ornamental leaves and flowers.
The berries turn from green to dark purple as they ripen. You can look for black elderberries as they are the ripe ones. Sometimes, they also appear as red elderberries.
Some of the varieties include American elder and the European elder.
The history of elderberries is as important to know as well.
What Is The History Of Elderberries?
Sites in Switzerland and Italy tell us that the black elderberry variety could have been the first elderberry to have been cultivated – and, that too, by prehistoric man.
In fact, Hippocrates, the ancient Greek who is known as the Father of Medicine, described the elderberry plant as his medicine chest. The fruit is native to Europe and North America. The berries have a long history of being used in folk medicine and are being researched for more than two decades for their medicinal benefits and are also used as a natural remedy thereby improving health and wellness.
 Did You Know?
Did You Know?There is a reason they are being researched – thanks to their varied nutritional profile.
What Is The Nutritional Profile Of Elderberries?
| Nutritional value per 100 g (3.5 oz) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Energy | 305 kJ (73 kcal) | |||||||
| Carbohydrates | 18.4 g | |||||||
| Dietary fiber | 7 g | |||||||
| Fat | 0.5 g | |||||||
| Protein | 0.66 g | |||||||
| Water | 79.80 g | |||||||
| Vitamin A equiv. | 30 μg (4%) | |||||||
| Thiamine (vit. B1) | 0.07 mg (6%) | |||||||
| Riboflavin (vit. B2) | 0.06 mg (5%) | |||||||
| Niacin (vit. B3) | 0.5 mg (3%) | |||||||
| Pantothenic acid (B5) | 0.14 mg (3%) | |||||||
| Vitamin B6 | 0.23 mg (18%) | |||||||
| Folate (vit. B9) | 6 μg (2%) | |||||||
| Vitamin C | 36 mg (43%) | |||||||
| Calcium | 38 mg (4%) | |||||||
| Iron | 1.6 mg (12%) | |||||||
| Magnesium | 5 mg (1%) | |||||||
| Phosphorus | 39 mg (6%) | |||||||
| Potassium | 280 mg (6%) | |||||||
| Zinc | 0.11 mg (1%) | |||||||
One ounce of elderberries (28 grams) contains 20 calories, 5.2 grams of carbohydrates, and 0.1 grams of total fat. Other nutrients in elderberries include
- 1 milligrams of vitamin C (17% of the daily value)
- 168 IU of vitamin A (3% of the daily value)
- 1 milligrams of vitamin B6 (3% of the daily value)
- 4 milligrams of potassium (2% of the daily value)
- 4 milligrams of iron (2% of the daily value)
Additionally, elderberries can be a great addition to your diet if you are looking for a fiber-rich fruit that can boost your digestive system. A single serving of elderberries is just enough to meet 28% of your daily fiber requirements.
Elderberries have an incredibly high polyphenol content. These are organic compounds that may work as anti-inflammatory, antioxidant agents to help improve blood glucose levels, blood pressure, and cardiovascular health. An experiment conducted on different varieties of berries showed remarkable levels of polyphenols in them. Black elderberry ranks second highest in comparison.
Total Polyphenol Content In Different Types Of Berries
Source: https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/food-science/berry-fruit Did You Know?
Did You Know?These nutrients are what make elderberries worth taking a look at. But what is elderberry good for? Let us find out.
What Are The Health Benefits Of Elderberries?
The antioxidants and flavonoids in elderberries contribute to most of their benefits. They boost immunity, protect the heart, and prevent cancer. The berries also improve skin and hair health. The fiber in these berries improves digestion and prevents other digestive ailments.
1. Boost Immunity

Several studies speak of the ability of elderberries to boost the immune system. One report published by the University of Maryland Medical Center talks about the powerful immune-boosting effects of elderberries (1).
The same is true with elderberry syrup as well, which increases antioxidant levels in the body and helps fight disease. The vitamins A and C in the fruit help maintain optimal health. Elderberries also offer protection against viruses that might damage cell walls.
The fruit also decreases mucus production during respiratory infections like cold and flu, easing the symptoms. And it is one excellent remedy for the debilitating symptoms of influenza, as per a Japanese study (2). Elderberries boost immunity by increasing the production of inflammatory cytokines (3). And this way, they also help treat upper respiratory tract infections and other respiratory ailments.
According to a study, Elderberry, a popular herbal supplement, can modulate inflammatory cytokines and possesses antiviral properties, even against SARS-CoV-2. In the United States, elderberry supplement sales increased by 415% in a single week in March 2020. In-vitro studies have shown the inhibitory effect of elderberry extracts against influenza viruses, with significant improvements in symptoms observed within two days. Although elderberry has potential, concerns exist about overstimulating the immune system and triggering cytokine storms. More research is needed, particularly for COVID-19 patients, before considering elderberry as a therapeutic intervention.
2. Improve Digestive Health
Though research is limited here, elderberries, like most fruits, are good sources of fiber and can enhance digestion. The fiber in the fruit can also treat other digestive issues like constipation, stomach upset, gas, and bloating.
3. Can Help Prevent Cancer
Scientists from numerous parts of the world had used elderberries in cancer treatment, with much success. This can be attributed to the quercetin in elderberries – whose therapeutic effects can stimulate the immune system and aid the treatment (4).
Other studies show that elderberries can also treat prostate cancer. The berries are known to inhibit a biochemical process called hedgehog signaling, which has been linked to cancer (5).
4. Enhance Heart Health
Given that they are rich in potassium (and also they have a great potassium to sodium ratio), elderberries can help regulate blood pressure. They ensure the blood vessels relax. Also, a high potassium diet is known to reduce the strain on the heart. Studies have shown that individuals taking a high amount of potassium (and by this, we don’t mean excess) had a 49 percent less risk of death by ischemic heart disease.
Some sources also say that elderberries can help regulate cholesterol levels and even boost circulation (and this offers good exercise to the heart and keeps it in shape), thereby improving cardiovascular health.
Elderberries also contain beneficial compounds called anthocyaninsi XColored water-soluble pigments that belong to the phenolic groups (plant compounds) and change color depending on their pH. , which protect the inner layer of the blood vessels from oxidative stress. This protects the cells from inflammatory stressors, ultimately improving circulation and cutting the risk of heart disease (6).
And not just elderberries, but several studies have proven time and again that all berries, in general, can have powerful protective effects on the heart (7).
5. Can Help Treat Diabetes
Reports suggest that elderberries can help lower blood sugar levels, aiding diabetes treatment (8). However, studies are limited in this regard, and we advise you to talk to your doctor first.
6. Strengthen Bones
The calcium, iron, and potassium in the berries are known to strengthen bones and increase bone mineral density, cutting the risk of osteoporosisi XA bone disease that makes bones brittle and weak due to low bone density and decreased bone mass which worsens with age. as a result.
Additionally, the anthocyanins in the berries might prevent bone loss in certain cases (9). As of now, we need more clarity on this. But do consult your doctor.
7. Can Aid Weight Loss
Just like most fruits, elderberries are rich in fiber. And fiber, as we know, improves satiety and can aid weight loss. This has been proven by a German study as well – where participants taking elderberry juice enriched with elderberry flower and the extracts saw a significant improvement in weight regulation.
8. Improve Skin And Hair Health
Infused with innate anti-aging and free radical fighting properties, elderberries keep your skin radiant for longer periods. Furthermore, they also act as a natural detoxifying agent and help prevent distressing skin conditions like breakouts, boils, and scars.
The anthocyanins in elderberries (the compounds that give them their characteristic red color) were found to give a natural boost to your skin’s health. This compound also protects against skin damage (10). In fact, distilled elderberry flower water is known to restore skin health and lighten the freckles (11). Applying the fruit extract can also reduce inflammation and bruising. The extract can help treat herpesi XA skin condition caused by the herpes simplex virus that leads to cold, contagious sores mostly around the mouth or genitals. as well. The antioxidants in the berry can fight the herpes virus and give relief.
The berries work great for your hair as well. You can take some elderflower oil (you should be getting it in the market) and mix it with some of your other favorite oils. Apply on the problem areas of your scalp. The serum can treat split ends, problematic hairlines, and might even encourage hair growth.
9. Can Boost Vision Health
Being rich in vitamins A and B6, elderberries can help prevent serious vision ailments like glaucomai XA group of eye conditions that damage the optic nerve due to high blood pressure. Constant eye pain is a symptom. and macular degenerationi XA common eye disorder that causes blurred vision due to damage to the inner layers of the macula in people above the age of 50. . The antioxidant activity of elderberries also helps ensure vision health in the long run.
10. Help Treat Urinary Tract Infections
Though there is very limited research on this, certain sources note that infusions of elderberry juice can help reduce inflammation in the urinary tract and treat urinary tract infections.
11. Fight Inflammation
Numerous studies talk about the anti-inflammatory properties of elderberries. In fact, the berries have even been used to treat eye inflammation.
Another study states how anthocyanins in elderberries can help fight inflammation (12). They achieve this by fighting oxidative stress.
12. Improve Brain Health
One study talks about how the anthocyanins in berries (including elderberries) can help treat cognitive impairment and the resultant conditions like Alzheimer'si XA progressive neurodegenerative disease in which brain cells shrink and impair cognitive function and memory. (13).
Elderberries are also replete with quercetin, which is an important flavonoid critical for brain health. Quercetin reduces the harmful inflammation at a cellular level. It also activates the mitochondria in your cells – which are powerhouses that boost cell health and improves cognitive function.
13. Alleviates Cough
Research shows that elderberry may aid cough reduction. It contains anti-inflammatory anthocyanins that may help reduce the cold duration while treating symptoms such as fever, cough, and pain(14). You can also take elderberry for a sore throat and stuffy nose seen during a common cold and flu.
14. Soothes Allergies
Elderberry extracts are loaded with antioxidants and possess strong antiviral and antibacterial properties (15). They may impact the course of some diseases by reducing their damaging oxidative stress and improving the body’s immune responses (16). Studies show that a diet rich in antioxidants may lower the risk of allergic disease such as rhinitis (17).
That’s with the benefits. But there are other ways you can use elderberries.
What Are The Other Uses Of Elderberries?
- The berries can be used to prepare teas, tinctures, wine, jams, and syrups. Elderberry wine is a popular add-on to meals.
- The flowers of the elderberry plant are used to make jelly. They can also be used in baking.
- The elderberry flowers are also used internally for treating influenza and skin irritation.
We know you want to take elderberries right away, seeing these benefits. But there is something else in store for you.
How To Select And Store Elderberries
Selection
Ensure you pick berries that are firm and have a deep color. Avoid those that are mushy or bruised.
Storage
Remove the mushy or moldy berries, if any, from the lot – and then store them in the refrigerator in their original packing for about a week. Wash the berries before you use them.
What would you do once you have picked the right berries and stored them properly? You would incorporate them into your diet – which is quite simple. You can either add them to your salad or pancakes and honey. Or you can eat them whole. Even elderberry juice or smoothie would be a great start.
Jennifer Hilado, a blogger, shared her experience about taking an elderberry supplement to boost her immune system. She said, “I’m a big believer in elderberry and all the benefits it provides. It has kept my children and me healthy since we began using it and I’ll never go back (i).” She added, “Colds are few and far between and when they do catch one, it’s a lot less severe. In the times we live in now, I am so thankful to have a powerful tool like this to keep my kids healthy.” She preferred using an elixir and adding it to tea or juice, as she described: “You can buy it in a form that’s already cooked and prepared for you, or you can buy the dried berries and make it into anything you can think of.”
We have something that’s getting popular by the day.
How To Make Elderberry Tea
Making elderberry tea is quite simple. Follow this easy recipe and enjoy the elderberry tea benefits.
What You Need
- 1 cup of water
- A few elderberries
- A pinch of turmeric and cinnamon
Directions
- Firstly, add water and elderberries to a saucepan. You can also add turmeric and cinnamon.
- Bring to a boil and simmer for about 15 minutes.
- Let the liquid cool. Strain the berries using a strainer. Your tea is ready.
You can also make the tea by boiling 3-5 grams of elderflowers in 250 mL of water. Or if you are using the bark, take one teaspoon of it and add to half a cup of boiling water.
And yes, you can try these sumptuous elderberry recipes as well.
Any Popular Elderberry Recipes?
1. Simple Spiced Elderberry Syrup
What You Need
- 1 cup of fresh elderberries
- 3 cups of water
- 2 tablespoons of freshly sliced ginger
- 1 teaspoon of cinnamon
- 1 teaspoon of cloves
- 1 cup of raw honey
Directions
- Except for honey, place the other ingredients in a pot. Bring it to a boil and reduce to a simmer for about an hour.
- Remove the pot from the heat. Using a mesh sieve, strain the liquid. Transfer the liquid to a jar and stir in a cup of honey.
- Keep the jar sealed in the fridge for about a couple of weeks.
2. Elderberry Soup
What You Need
- 5 ounces of elderberries
- 1 quart of water
- 1 ½ teaspoons of cornstarch
- ½ pound of peeled and diced apples
- 1 lemon peel
- White sugar, to taste
Directions
- Place the elderberries in a pot containing 2 cups of water. Bring to a boil. Simmer for 10 minutes. Remove from the heat, puree in a blender, and bring it back to the pot.
- In a bowl, mix the cornstarch with a tablespoon of the puree and stir into the pot to thicken.
- In a separate pot, bring the apples and the remaining water to a boil. Place the lemon peel inside the pot. Simmer for 10 minutes. Remove the peel, mix the elderberry puree with the apple mixture, and add sugar.
These recipes are sure to taste great. And will definitely make a healthy snack as well. But wait, how many elderberries can you have in a day?
What Is The Recommended Dosage Of Elderberries?
Though there is not enough information with respect to regular dosage, for treating conditions like influenza, you can take 15 mL of elderberry syrup 4 times a day for 5 days.
For kids suffering from flu, the dosage is 5 mL of elderberry extract, twice a day. And for adults, it is 10 mL, twice a day. You can also have 4 elderberries for 48 hours without the risk of any side effects.
Any Interesting Elderberry Facts?
- An elderberry can grow in the form of a shrub or a small tree.
- An elderberry tree produces 12-15 pounds of berries in a year.
- In the European countries, the elderberry fruit is used in the manufacture of wine and brandy.
- Elderberry is a perennial plant that can survive for 80-100 years in the wild.
- Crushed elderberry leaves release an unpleasant smell, and these can repel flies.
Now to another important question – where can you get your elderberries from?
Where To Buy Elderberries
You can pick the berries from the neighborhood supermarket or procure them online.
You can also take elderberry supplements after consulting your doctor.
Elderberries, just like all berries, taste great and are extremely beneficial. But they have certain side effects as well.
What Are The Side Effects Of Elderberries?
- Nausea Or Vomiting
Consuming elderberries when they are raw and unripe might cause nauseai XAn uncomfortable feeling in the stomach that causes an urge to vomit but does not always lead to vomiting. and vomiting. In certain cases, it might also lead to severe diarrhea.
- Autoimmune Diseases
The berries might cause the immune system to become more active, so much that it might even increase the symptoms of autoimmune diseases – where the immune system attacks the body. Some of the autoimmune diseases include multiple sclerosisi XA disorder in which the immune system attacks the protective covering of the nerves and causes impaired coordination, and fatigue. andrheumatoid arthritisi XA chronic autoimmune disease that affects the joints of hands and legs and causes inflammation of joints and pain due to swelling. .
- Issues With Pregnancy And Breastfeeding
We have less information on the safety of elderberries during pregnancy and breastfeeding. So stay safe and avoid use.
Infographic: How To Use Elderberries?
Elderberries are known for their medicinal properties. They have a long history in folk medicine and are used in the supplement form for treating ailments like cold and flu. In addition, the berries can be used to make jams, tea, or syrups. Click on the infographic below to learn how to use these berries. Illustration: StyleCraze Design Team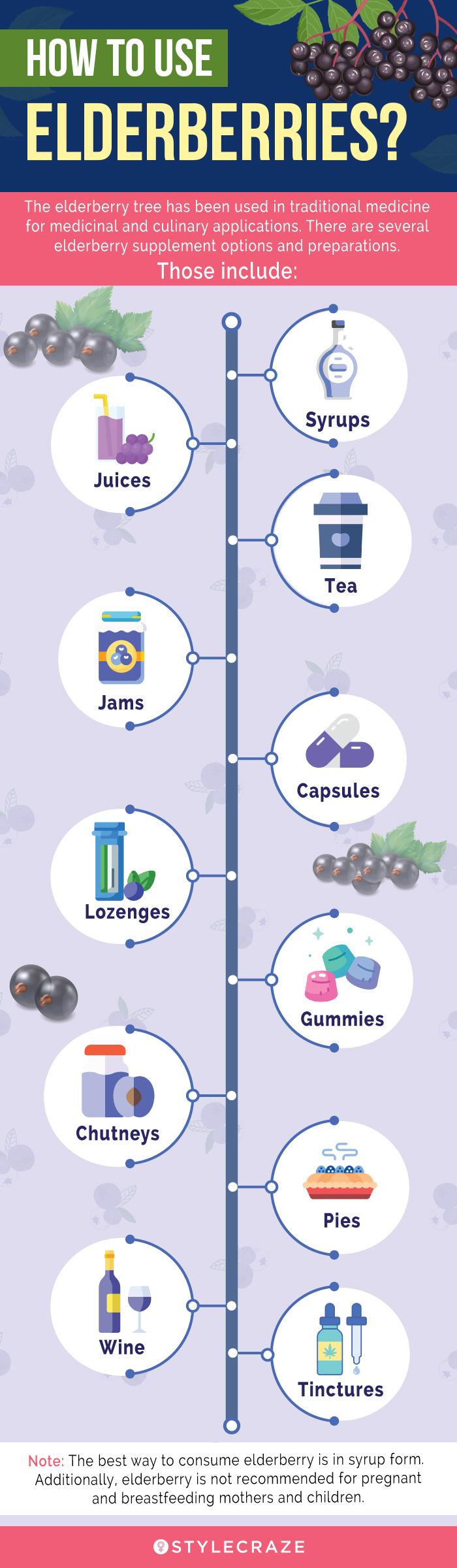
Elderberry benefits are many. These benefits can be attributed to their antioxidant content. These berries can boost immunity and improve digestive, heart, skin, hair, vision, and brain health if regularly included in the diet. They also reduce cancer risk, combat inflammation, manage urinary tract infections and diabetes, strengthen bones, and aid in weight loss. However, overconsumption may cause nausea or vomiting and trigger autoimmune diseases (though rare). Hence, moderate consumption is advised. You can include elderberries in your diet with any of the aforementioned recipes.
Frequently Asked Questions
What do elderberries taste like?
Fresh elderberries usually have a tart taste. They taste sour and acidic or somewhat like a lemon.
Are elderberries poisonous?
The seeds, leaves, stems, and roots of elderberries contain a cyanide-inducing glycoside, which might make one extremely ill. Take precautions and consult your doctor before taking any of these for medical reasons. Elderberry bushes are poisonous. The elderberry bark might also be poisonous in high amounts – however, it has strong laxativei XSubstances that increase the bulk of the stool and increase bowel movements by loosening it, relieving temporary constipation. effects.
How to plant elderberries?
Check your soil pH first (you can contact your local County Extension Office) for this purpose. The pH must be between 5.5 to 6.5. They grow best in fertile, moist, and well-drained soil. You can pick a location with full sun. Plant elderberries at least 8 feet apart in rows 10 feet apart. Ensure you water the plant thoroughly. And no fertilizers in the first year.
What are the benefits of elderberry syrup?
Same as elderberries.
How does elderberry compare to other natural remedies for the same health conditions?
Elderberries have more anthocyanins than most fruits and berries, which makes them beneficial for heart health as they protect the cells from inflammation and resulting heart problems (14).
What are some creative and innovative ways to incorporate Elderberry into food and beverages for added health benefits?
Apart from Elderberry syrup and soup, you can make smoothies, ice creams, and teas. They also make an excellent addition to your pies or cupcakes.
Key Takeaways
- Elderberries have been around since prehistoric times and have been used for their medicinal benefits.
- Elderberries boost digestive and heart health, improve immunity, and strengthen bones.
- It has antioxidant properties that improve skin health. It boosts hair growth and repairs split ends.
- Avoid unripe berries as they may upset the stomach, cause vomiting, and lead to severe diarrhea.

Image: Stable Diffusion/StyleCraze Design Team
Learn about the amazing health benefits of cilantro and discover how this flavorful herb can help improve your nutrition and overall health. Watch the full video here.
Personal Experience: Source
StyleCraze's articles are interwoven with authentic personal narratives that provide depth and resonance to our content. Below are the sources of the personal accounts referenced in this article.
i. The Impressive Magic of Elderberry: One Mom’s Quest for Better Health for Her Familyhttps://jhilado.medium.com/the-impressive-magic-of-elderberry-one-moms-quest-for-better-health-for-her-family-8fc9841b89a8
References
Articles on StyleCraze are backed by verified information from peer-reviewed and academic research papers, reputed organizations, research institutions, and medical associations to ensure accuracy and relevance. Read our editorial policy to learn more.
- “Elderberry”. University of Maryland Medical Center.
- “Anti-influenza effects of elderberry juice…”. US National Library of Medicine.
- “Berries: emerging impact on cardiovascular health”. US National Library of Medicine.
- “The effect of Sambucol…”. US National Library of Medicine.
- “Elderberry showcase”. University of Missouri.
- “Anthocyanins”. Pennington Nutrition Series.
- “Berries: emerging impact on cardiovascular health”. US National Library of Medicine.
- “Elderberry”. University of Maryland Medical Center.
- “The role of antioxidant rich berries…”. University of Arkansas.
- “Anthocyanins, Vibrant Color Pigments, and Their Role in Skin Cancer Prevention“. US National Library Of Medicine.
- “Common elderberry”. USDA.
- “Black elderberry extract…”. US National Library of Medicine.
- “Nutraceuticals in cognitive impairment and…”. US National Library of Medicine.
- “Sambucus nigra (black elder) as alternative treatment for cold and flu…” US National Library of Medicine
- “Elderberry supplementation reduces cold duration…” US National Library of Medicine
- “Advanced research on the antioxidant and health benefit…” Journal of Functional Foods
- “Role of antioxidants on the clinical outcome of patients…” US National Library of Medicine































