15 Foods Rich In Omega-3 Fatty Acids That You Should Eat
Besides fish, there are many other food sources rich in omega-3 that you can eat!
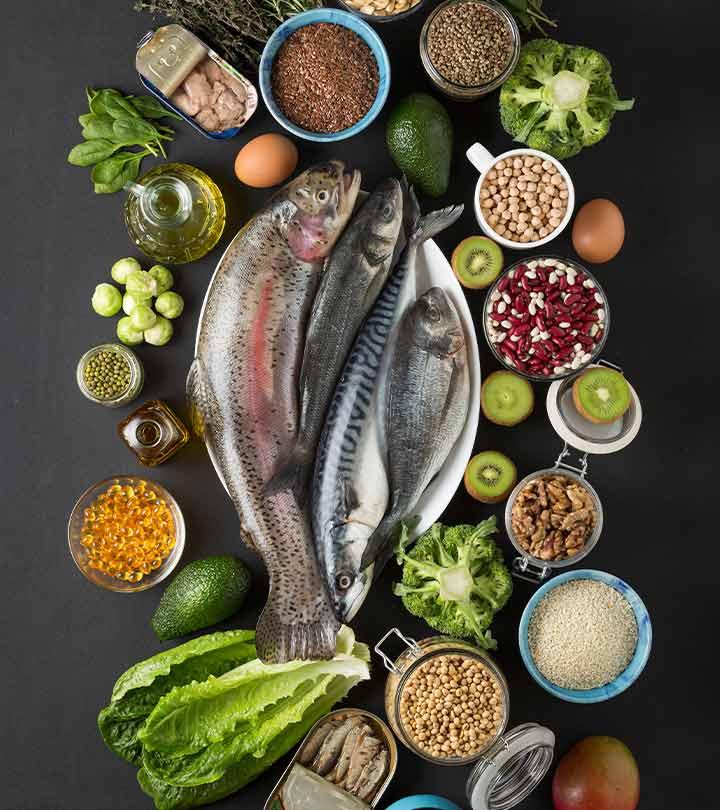

Image: Shutterstock
Omega-3 fatty acids are becoming increasingly popular for the array of health benefits they offer. These essential nutrients can impact the physical and mental well-being of an individual. Consuming foods high in omega-3 fatty acids helps improve the functioning of cells and membranes (1). It also helps maintain the metabolism of glucose and cells. Studies also suggest that intake of omega-3 fatty acids for more than six weeks may increase the body’s metabolic rate and decrease total body fat (2).
In this article, we discuss the 15 foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids and their health benefits. Keep reading!
In This Article
What Are Omega-3 Fatty Acids?
Omega-3 fatty acids are polyunsaturated fatty acids that are essential for the body. Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) are the two major types of long-chain omega-3 fatty acids. Seafood is the main source of EPA and DHA (2).
The body also synthesizes small amounts of EPA and DHA from alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), an omega-3 fatty acid found in flaxseed, canola, and walnuts. The body also forms docosapentaenoic acid (DPA) –also a long-chain omega-3 fatty acid–when it breaks down (metabolizes) DHA (3).
A healthy adult should consume at least two portions of fish a week to obtain its health benefits, according to the UK Scientific Advisory Committee on Nutrition (4).
Learn about the health benefits of omega-3 fatty acids in the next section.
Health Benefits Of Omega-3 Fatty Acids
1. May Help Combat Depression
The deficiency of omega-3 fatty acids is linked to an increased risk of various psychiatric disorders, including depression (5). Depression is a multifactorial disorder, and depression due to insufficient omega-3 fatty acid intake can be of one type. People suspected to have this type of depression may respond well to a diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids with no significant side effects (6).
2. May Reduce The Risk Of Cardiovascular Diseases
Omega-3 fatty acids protect the heart and reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease by reducing high LDL cholesterol and blood clotting. The intake of omega-3 fatty acids may help reduce the risk of sudden death caused by cardiac arrhythmias (irregular heartbeat). Besides, it may also reduce all-cause mortality in people with known coronary heart diseasei XA heart condition in which plaque build-up can block the arteries from delivering blood to the heart. .
An online survey conducted on 834 young adults found that 83% recognized the association between omega-3 fatty acids and brain and heart health. Furthermore, 48% of the respondents reported purchasing or consuming omega-3 foods, while 21% of the participants consumed omega-3 supplements.
Omega-3 fatty acids are also used to treat hyperlipidemia (high cholesterol levels) and hypertensioni XA common condition in which the force of blood against artery walls is higher than normal. It is also known as high blood pressure (HBP). – which cause cardiovascular disease (7).
The American Heart Association recommends at least one serving of fish daily for those with coronary heart disease. It also recommends two servings of fish per week for persons with no coronary heart disease (7).
3. May Help With Cancer Treatment
Inflammation causes tumors and their growth. Omega-3 fatty acids have anti-inflammatory properties, and their intake may increase the efficacy of chemotherapy. These fatty acids are shown to preserve muscle mass and function in cancer patients even during active treatment. A combination of chemotherapy and supplementation of omega-3 fatty acids may enhance the treatment outcome (8).
4. May Help Reduce Cholesterol
Elevated triglycerides (fats) may lead to hypertriglyceridemia (high-fat concentration in the blood). Managing LDL cholesterol levels helps manage triglycerides effectively. Omega-3 fatty acids like EPA and DHA are proven to reduce triglycerides levels (9).
 Quick Tip
Quick TipWhy take supplements when you have other alternatives? Here are 15 foods you can eat to get omega-3 fatty acids naturally. Read on!
15 Foods High In Omega-3 Fatty Acids
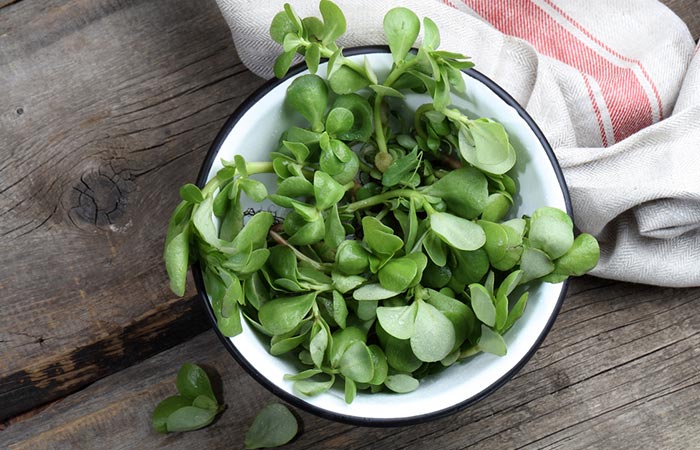
1. Purslane
Purslane (a leafy green vegetable) is richer in omega-3 fatty acids than spinach. Fresh purslane leaves (100g) contain about 300-400 mg of alpha-linolenic acid (10). Including it in your diet may help you get a sufficient amount of omega-3 fatty acids.
2. Walnuts
Walnut is one of the healthiest nuts that contain the highest amount of omega-3 fatty acids (11). These nuts can also be a tasty addition to your diet.
3. Brussels Sprouts
Brussels sprouts resemble miniature cabbages and are low in calories. They contain a significant amount of omega-3 fatty acid content (12).
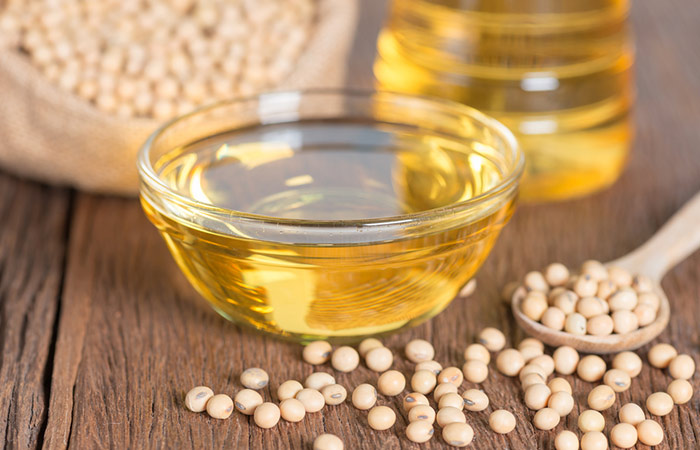
4. Soybean Oil
The protein-rich soy is popular in many diets. Soybean oil is found to contain a significant amount of omega-3 fatty acids (13). However, more research is warranted to understand the benefits of omega-3 fatty acids from soy.
Research shows that olive oil and canola oil are also all good sources of omega fatty acids and can be a substitute for soybean oil (14).
5. Seeds
Seeds like chia seeds flaxseed are high in omega-3 fatty acids. Their oil extracts are also used in omega-3 supplements. Sprinkling these oils or ground seeds over salads or smoothies is an easy way to include them in a regular diet (15).
6. Egg Yolks
Many people don’t prefer egg yolks due to their high-calorie content. But, they contain a significant amount of omega-3 fatty acids (16). So, add egg yolks to your diet in moderation.
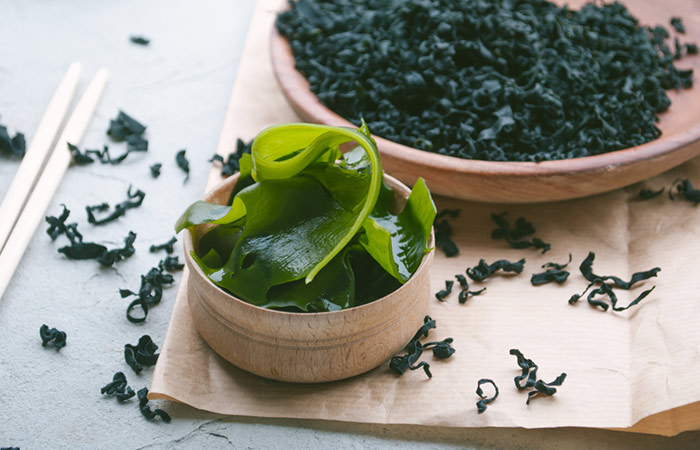
7. Seaweed
Seaweed, like algae, is a great source of nutrients for people who prefer plant-based foods. They are rich in omega-3 fatty acids, which help prevent inflammatory, cardiovascular, and nervous system disorders (17).
8. Fish
Oily fish, fatty fish, cold-water fish, salmon, tuna, sardines, and mackerel are rich in omega-3 fatty acids. They are also rich in proteins and vitamins, and may help lower the risk of many health conditions (18). Cod liver oil, extracted from the liver of codfish, is also a rich source of omega-3 fatty acids, essential for maintaining good health (19).
9. Wild Berries
Different kinds of wild berries contain significant amounts of omega-3 fatty acids (20). They can be used as toppings on smoothies or consumed as an evening snack.
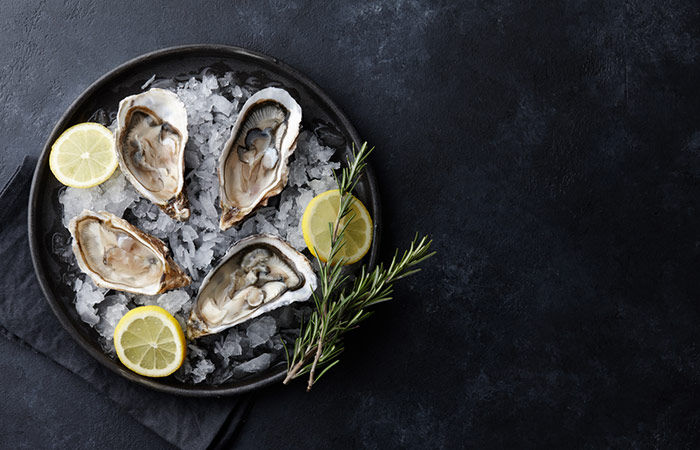
10. Oysters
Oysters are rich in many nutrients. 100 g of oysters contain 188 mg of eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and 203 mg of docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) (21).
11. Scandinavian Caviar Paste
Scandinavian caviar paste is a spread naturally enriched with omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (22). It is used in making sandwiches, tapas, soups, and as a spread on toasted bread.
12. Wild Rice
Wild rice grows in the shallow waters of North America and differs from brown and white rice. 100 g of wild rice provides 300 mg (0.3g) of omega-3 fatty acid (23).
13. Winter Squash
Winter squash (100g) contains 26 mg of omega-3 fatty acids (24). This seasonal fruit can be a healthy inclusion in your diet.
14. Hemp Seeds
Hemp seeds are a rich source of omega-3 fatty acids. They have also been found to improve cardiovascular health (25). You can add them to smoothies and salads or consume raw.
15. Spinach
Spinach and kale are good sources of omega-3 fatty acids (26). You can make spinach dishes or add some spinach leaves to your juices or smoothies.
 Quick Tip
Quick TipIn the next section, we discuss how much omega-3 fatty acid you need in a day. Read on!
How Much Omega-3 Fatty Acid Do You Need Per Day?
Per Day?
The required intake of omega-3 fatty acid foods varies from person to person. However, it ranges between 200-500 mg (both EPA and DHA) per day for adults (28).
Pregnant women need 650 mg of omega-3 fatty acids every day, of which 300 mg should be DHA. Depending on the amount of omega-3 foods consumed during the week, pregnant women would need an additional 400 to 550 mg of omega-3 PUFAsi XShort for polyunsaturated fatty acids, they are essential for cell growth and are obtained from external nutritional sources. (EPA and DHA) daily. Of this, about 225 mg should be DHA (29).
Anthony Puopolo, Chief Medical Officer and Physician at LifeMD, says it is in general agreement that 250-500mg of omega-3 fatty acids is a healthy amount for adults to consume daily. This can be achieved simply through diet or through fish oil tablets or other supplements.
Like any other dietary supplement, omega-3 fatty acids also may cause certain side effects. Learn more about them in the next section.
Side Effects Of Omega-3
Omega-3 fatty acids are generally safe for consumption. However, avoid them if you are allergic to fish or seafood. You may instead consider plant-based omega-3 sources like flaxseeds.
Omega-3 fatty acid supplements may also cause burps with a fishy aftertaste, indigestion, diarrhea, gas, constipation, abdominal pain, nausea, and rashes. They may even lead to pain in the oropharyngeal area (the middle part of the throat behind the mouth). The supplements may also interact with certain medications that help prevent blood clots (2). Therefore, it is recommended to consult your doctor before starting omega-3 supplementation.
Infographic: 10 Superfoods Packed With Omega-3
Incorporating omega-3 fatty acid foods into your diet can have a positive impact on your overall well-being, from reducing the risk of cardiovascular issues and fighting depression to reducing cholesterol. The infographic below lists 10 delicious options you should add to your diet that pack a punch of omega-3 goodness. Check it out!

Illustration: StyleCraze Design Team
Save the high-quality PDF version on your device now.
Download Infographic
Omega-3 fatty acids are essential nutrients that offer an array of health benefits. Consuming foods with omega-3 fatty acids helps treat depression and enhance cancer treatment outcomes. They may also lower cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease. While many people prefer taking them in supplemental form, they can also be consumed through the foods listed above. Add any of these foods to your diet to meet your daily requirement of omega-3 fatty acids.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is avocado high in omega-3?
Yes, avocados are a good source of omega-3 rich foods that also account for their antioxidant properties (28).
Does milk have omega-3?
Recent research suggests that organic milk from grass-fed cows contains about 147% more omega-3 fatty acids than conventionally fed cows (31).
Do almonds have omega-3?
While almonds have reasonable amounts of monounsaturated fatty acidsi XA type of unsaturated dietary fat with a single, carbon double bond which can help reduce bad cholesterol. , they only have traces of omega-3 fatty acids (32). Walnuts and pecans are better options for omega-3 fatty acids.
Does yogurt have omega-3?
Yes, you can find yogurt varieties fortified with omega-3 fatty acids (33).
Does chicken have omega-3?
Chickens fed a diet fortified in omega-3 fatty acids can have a good amount of this heart-healthy nutrient.
Key Takeaways
- Omega-3 fatty acids can protect your heart by lowering cholesterol levels in your body.
- Omega-3 supplementation along with chemotherapy can aid cancer treatment.
- You can eat foods such as walnuts, soybeans, egg yolk, fish, and oysters to increase your omega-3 intake.
- These may be a good remedy for depression. However, it is advisable to consult with your doctor beforehand.
Learn about the top omega-3 foods for your low-carb diet! Click on the video to discover which foods are best for your health and weight loss goals.
Sources
Articles on StyleCraze are backed by verified information from peer-reviewed and academic research papers, reputed organizations, research institutions, and medical associations to ensure accuracy and relevance. Read our editorial policy to learn more.
- The science behind dietary omega-3 fatty acids
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC2174995/ - Omega-3 Fatty Acids
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK564314/ - Omega-3 Supplements and Cardiovascular Diseases
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4153275/ - Omega-3 fatty acids: a comprehensive review of their role in health and disease
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19329703/ - Omega-3 fatty acids and mental health
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S241464472030004X - Omega-3 fatty acids and the treatment of depression: a review of scientific evidence
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5481805/ - Omega-3 fatty acids and cardiovascular disease
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25720716/ - Omega-3 fatty acids in cancer
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23299701/ - Overview of Omega-3 Fatty Acid Therapies
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC3875260/ - Common purslane: a source of omega-3 fatty acids and antioxidants
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/1354675/ - Nuts omega-3s and food labels
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC522631/ - Omega-3 Versus Omega-6 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids in the Prevention and Treatment of Inflammatory Skin Diseases
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC7037798/ - Omega-6 and omega-3 oxylipins are implicated in soybean oil-induced obesity in mice
https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/174270/nutrients - The Dietary Replacement of Soybean Oil by Canola Oil Does Not Prevent Liver Fatty Acid Accumulation and Liver Inflammation in Mice
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7760057/ - Antioxidant capacity and chemical composition in seeds rich in omega-3: chia flax and perilla
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/260763621 - Comparative omega-3 fatty acid enrichment of egg yolks from first-cycle laying hens fed flaxseed oil or ground flaxseed
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6280955/ - Polyunsaturated fatty acids in various macroalgal species from north Atlantic and tropical seas
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3131239/ - Fish Consumption Fish Oil Omega-3 Fatty Acids and Cardiovascular Disease
https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/full/10.1161/01.CIR.0000038493.65177.94 - Clinical application of omega-3-fatty acids (cod-liver oil)
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16320848/ - Wild berries: a good source of omega-3
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16900081/ - Mollusks oyster eastern farmed raw
https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/175172/nutrients - Effects of Scandinavian caviar paste enriched with stable fish oil on plasma phospholipid fatty acids and lipid peroxidation
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12947422/ - Wild rice raw
https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/169726/nutrients \ - Squash winter butternut raw
https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/169295/nutrients - The cardic and hemostatic effects of dietary hempseed
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC2868018/ - Extraction and Natural Bioactive Molecules Characterization in Spinach Kale and Purslane: A Comparative Study
https://www.mdpi.com/1420-3049/26/9/2515/htm - Omega-3 Fatty Acids
https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Omega3FattyAcids-Consumer/#h6 - Omega-3 Fatty Acid Intake by Age Gender and Pregnancy Status in the United States: National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2003–2014
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6356780/ - Omega-3 Fatty Acid Supplementation During Pregnancy
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2621042/ - Fatty Acid Profile, Total Carotenoids, and Free Radical-Scavenging from the Lipophilic Fractions of 12 Native Mexican Avocado Accessions
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31482386/ - Enhancing the fatty acid profile of milk through forage‐based rations, with nutrition modeling of diet outcomes – Benbrook – 2018 – Food Science &
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/fsn3.610 - Nuts, almonds, oil roasted, lightly salted
https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/168602/nutrients - Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids Added to Yogurt – ScienceDirect
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780128051344000079#:~:text=(2007)%20reported%20that%20yogurt%20can,20%E2%80%9360%20mg%20per%20serving